Editorial notice
Clinical oncology is currently undergoing a period of unprecedented change. Targeted therapy, and subsequently immunotherapy, has revolutionized the clinical course and outcome of many patients with solid cancer. Clinical oncology is inseparable from molecular oncology, the development of which is interconnected. Molecular tumor research proposes the most precise, effective and lesser toxic antitumor therapy regimen is an extremely urgent clinical task, especially in life-threatening and resistant to other types of treatment cases of cancer. Modern technologies of genomic and postgenomic studies, as well as molecular imaging methods (positron and single photon emission computed tomography, PET and SPECT, respectively) make it possible not only to assess the metabolic and receptor status of tumor foci, but also to select the optimal therapeutic tactics as a key to the lock. In the clinical practice of oncology, there is an increasing need for molecular tumor board (MTB). Published real clinical experience with MTB-recommended treatment regimens based on the molecular geno-transcriptomic profile of the tumor indicates better relapse-free and overall patient survival compared to treatment prescribed by a physician without taking into account the molecular profile of the tumor. More experience is needed and randomized controlled clinical trials are needed for more solid and evidence-based conclusions. However, there is no doubt that the MTB is a powerful tool for the development of precision personalized oncology.
Clinical endocrinology
BACKGROUND: The issues of monitoring the effectiveness of iodine deficiency prevention programs are an important component in the process of iodine elimination. Neonatal thyrotropin (TSH) has been used as a criterion for the severity of iodine deficiency since 1994, however, the question of the “cut-off point” of the neonatal TSH level has been widely discussed in the recent literature.
AIM: Evaluate the criterion for neonatal hyperthyroidism above 5 mIU/l from the perspective of monitoring iodine deficiency and establish a «cut-off point» on the model of healthy pregnant women with adequate iodine status.
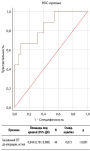
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A prospective study was conducted in a population of pregnant women in the city of Tyumen, with the formation of observation groups according to the level of iodine excretion in the urine — the main group (with adequate iodine status throughout the entire gestation period) and the comparison group (women with iodine levels less than 150 μg/l). The results of neonatal screening for congenital hypothyroidism in children of women participating in the study were evaluated. The frequency of neonatal TSH above 5mIU/l was assessed in the observation groups. ROC-analysis was performed and a «cut-off point» of the level of neonatal TSH was established as an indicator of iodine deficiency.
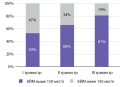
RESULTS: The median urinary iodine concentration in the population of pregnant women in Tyumen was 159.05 μg/l, the incidence of goiter was 0.38%, the incidence of neonatal hyperthyroidism above 5 mIU/l was 2.88%, which characterizes adequate iodine intake in the pregnant population women. The frequency of neonatal TSH above 5 mIU/l in newborns from women from the main group was 1.47%, and in the comparison group — 9.3% (p = 0.076). ROC analysis revealed a threshold value of neonatal TSH of 2.77 mIU/l at the cut-off point, which corresponded to the highest value of the Youden index. Urinary iodine concentrations greater than 150 μg/l were predicted for nTSH values below this value.
CONCLUSION: Analysis of databases of neonatal screening for congenital hypothyroidism makes it possible to effectively, quickly and at minimal cost annually assess the iodine status in the population. The established «cut-off point» of neonatal TSH in the model of healthy pregnant women with adequate iodine intake in our work is 2.77 mIU/l, the absence of statistically significant differences in the incidence of neonatal hyperthyroidism above 5 mIU/l from women with different iodine status during pregnancy indicate the need to revise the existing threshold of 5 mIU/l and may be an incentive to conduct large-scale studies in regions with different iodine supply.
BACKGROUND: Precise localization of abnormal parathyroid glands is important for a successful surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT). While a large number of patients can be successfully treated with the focused parathyroidectomy, there is a considerable rate of the persistent PHPT mostly because of undetected multiglandular disease (MGD).
AIM: The aim of the study was to evaluate the meaning of preoperative visualization data for planning the surgery for patients with PHPT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study was conducted at SPBU Hospital in 2017-2018. 810 patients who underwent a primary surgery for PHPT were included in the study. Preoperative imaging results were investigated and multivariative logistic regressions were calculated to assess the predictive values of preoperative data. The rate of cases with persistent disease and cases with MGD were compared between patients with different results of preoperative data.
RESULTS: Age, sex, body mass index, negative results of preoperative US, MIBI and 4D CT were not independently associated with the higher risk of multiglandular disease. The larger number of performed preoperative visualization studies were associated with the higher risk of persistence. 37% cases of MGD were not identified preoperatively. There were 7 cases with previously unsuspected second adenomas found only due to bilateral neck exploration.
CONCLUSION: Any combination of preoperative visualization modalities was not able to rule out the MGD reliably. Efficacy of surgical treatment was not associated with the higher number of preoperative studies. Bilateral neck exploration may decrease the rate of the persistent hyperparathyroidism improving the identification of multiglandular disease.
AIM: To determine significant factors affecting the survival of patients with ectopic ACTH syndrome (EAS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A multi-center, observational study with a retrospective analysis of patients with EAS. The end point of the study was the fatal outcome of patients from various causes. In order to identify predictors of survival or mortality, univariate and multifactorial Cox regression analyses were carried out. ROC-analysis was used to determine the prognostic threshold values of individual predictors. The survival analysis was carried out using the Kaplan-Mayer method. Statistical data processing was carried out by using IBM SPSS Statistics 23.
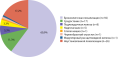
RESULTS: The age of patients at the time of diagnosis ranged from 12 to 76 years (Me 40 years [28;54]). The age of the studied population was 55 years [38; 64] for women and 42 years [32; 54] for men. The median period of observation was 50 months [13;91], with a maximum follow-up of 382 months. 92 patients (60,9%) had bronchopulmonary NET, 17 (11,3%) — thymic carcinoid, 8 — pancreatic NET, 5 –pheochromocytoma, 1– cecum NET, 1– appendix carcinoid tumor, 1 — medullary thyroid cancer and 26 (17,2%) patients had an occult NET. The primary tumor was removed in 101 patients (66,9%). Bilateral adrenalectomy was performed in 42 (27,8%) cases. Metastases were revealed in 23,2% (n=35) of patients. Relapse of the disease was observed in 24,4%, long-term remission was preserved in 64 patients (74,4%). Death occurred in 42 patients (28%). The average age of survivors was 47,0±15,2 versus 53,5±15,6 years for the deceased (p=0,022). The average survival time from diagnosis for the deceased was 32 months, Me 16,5 months [7;54]. Multivariate analysis revealed that the following factors have a direct impact on survival: age of diagnosis ≥51 years (OR 4,493; 95% CI 2,056–9,818, p<0,001), bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumor (NET) (OR 0,281; 95% CI 0,119–0,665, p=0,004), the presence of distant metastases (OR 2,489; 95% CI 1,141–5,427, p=0,022), late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC) ≥122,2 nmol/L (OR 2,493; 95% CI 1,014–6,128, p=0,047).
CONCLUSION: The prognosis of patients with EAS is influenced by the age of diagnosis, NET localization, distant metastases and level of LNSC. The most common cause of ectopic ACTH syndrome was bronchopulmonary NET which was associated with the best survival rate.
BACKGROUND: Pregnancy is a condition with important structural and physiological changes in the thyroid gland. In this regard, experts of thyroid associations have recommended developing specific reference intervals taking into account the natural and socio-geographical characteristics of the region under study.
AIM: To conduct an epidemiological analysis and evaluate TSH reference intervals in pregnant women living in the central regions of the Russian Federation with mild iodine deficiency.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We have conducted the observational multicenter cross-sectional study included 2008 healthy pregnant women at different trimesters of pregnancy, from three regions of the Russian Federation (Moscow, Ivanovo and Smolensk). We assessed the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, antibodies to serum thyroglobulin, the level of iodine concentration in the morning portion of urine (cerium arsenic method) and we have conducted a questionnaire (date birth and gestational age). Women with elevated titers of anti-TPO and/or anti-TG antibodies were excluded from the study (245 women). As a result, we assessed high and medium levels of TSH and its overestimation with iodine sufficiency in pregnant women. The results are presented using the calculation of 2.5 and 97.5 percentiles.
RESULTS: We confirmed the presence of iodine deficiency in the study areas. The median concentration of iodine in the urine was: in Moscow 106 μg/l, in Ivanovo 119 μg/l, in Smolensk 134 μg/l. Pregnant women were divided into 2 groups according to iodine adequacy. In the group with optimal iodine supply, the level of TSH was 0,006–3,36 in the 1st trimester, 0,20–3,74 in the 2nd trimester, and 0,33–3,68 mIU/L in the 3rd trimester. In the group with mild iodine deficiency — in the 1st trimester it was 0,11–3,00, in the 2nd trimester 0,22–3,78, in the 3rd trimester 0,07–3,04 mIU/l. Statistical analysis of the data revealed that when comparing the level of TSH by trimester, depending on the place of residence, no statistical difference was found (p = 0,239).
CONCLUSION: We obtained that the level of TSH in healthy pregnant women living in the central regions of the Russian Federation does not exceed 3.8 mIU/l in all trimesters.
Turner syndrome (TS) is a chromosomal disorder affecting female and characterized by complete or partial monosomy of the X chromosome. These genetic changes lead to the abnormalities in growth and development and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases, including those affecting the thyroid. Thyroid pathology in TS may include autoimmune thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis (Graves disease, AIT in the hyperthyroid state).
Thyrotoxicosis is the clinical syndrome of excess circulating thyroid hormones. One of the main causes of thyrotoxicosis is Graves’ disease (GD), an organ-specific autoimmune disease caused by the production of stimulating thyrotropin receptor antibodies. There are three treatment options for thyrotoxicosis: anti-thyroid drugs, radioactive iodine and thyroidectomy. A personalized approach to disease management is especially important in cases of genetic diseases.
We present a clinical case of a patient with TS and GD, who has been referred to a radiologist at the Department of Radionuclide Therapy of Endocrinology Research Center. The patient was diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism at neonatal screening, but thyroid hormones therapy was initiated aged three. Based on the survey, GD was diagnosed aged twenty one. Anti-thyroid drug therapy was started, which resulted in toxic hepatitis. Taking into account intolerance to anti-thyroid drugs, radioiodine therapy has been recommended, which led to hypothyroidism.
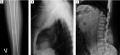
Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is a significant endocrine disease caused by increased production of parathyroid hormone (PTH) by altered parathyroid glands and violation of the mechanisms of regulation of serum calcium concentrations. These changes can lead to nephrolithiasis, osteoporosis, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, a number of less specific symptoms (nausea, vomiting, weakness, fatigue, etc.). Etiologically, in more than 85% of cases, PHPT is a consequence of sporadic solitary adenoma or hyperplasia parathyroid glands, however, in 1–3% of cases, the cause is carcinoma of parathyroid glands , including as part of various genetic syndromes. The importance of timely examination for PHPT of patients with characteristic clinical manifestations of this disease and — with an aggressive course — alertness towards carcinomas of parathyroid glands was noted. At the same time, the severity of the clinical picture and even the presence of suspicious signs characteristic of hereditary forms of carcinomas of parathyroid glands are not always a consequence of the malignant process. We present a description of a young patient with a severe course of PHPT, multiple fractures and a voluminous tumor of the upper jaw, developed as a result of a typical adenoma of parathyroid glands. Additionally, the algorithm of pre- and postoperative differential diagnosis for such patients is highlighted.
BACKGROUND. Neurosurgery is the most effective treatment for acromegaly. As most of the patients present with macroadenomas, surgical treatment is not always successful, even with the expert level of a neurosurgeon. Assessment of the postoperative remission rates in acromegaly preoperative predictors of treatment efficacy is an urgent task of modern research. AIM: To assess the short-term and long-term remission of acromegaly after endoscopic transnasal adenomectomy in a tertiary medical center and assess preoperative predictors of the treatment effectiveness.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A single-center, prospective, uncontrolled study was conducted. We included patients with active acromegaly who did not receive medical therapy with somatostatin analogues and were referred for endoscopic transsphenoidal adenomectomy. Plasma miRNA expression was assessed by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Postoperative samples of adenomas were sent for study, with the determination of the immunohistochemical staining for somatostatin receptors 2 and 5 subtypes and morphology was performed on postoperative adenoma samples.
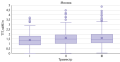
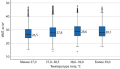
RESULTS: The study included 44 patients: 32.8% men, median age 47.0 [34.0; 55.0], IGF-1 744.75 ng/ml [548.83;889.85], growth hormone 9.5 ng/ml [4.94; 17.07]. Tumor volume 832 mm3 [419.25; 2532.38]. Early postoperative remission was achieved in 35 patients (79.5%). Patients who achieved short-term remission had higher IGF-1 and basal growth hormone levels. Median follow-up was 19.0 months [12.5;29.0]. Long-term remission was achieved in 61.4% (27 patients), no remission in 9 (20.5%), recurrency in 2 patients (4.5%), 6 patients were to follow-up (13.6%). In patients with long-term remission, we observed lower growth hormone and IGF-1 levels. No differences in miRNA expression was observesd. The predictive value of basal GH before surgery for long-term remission was assessed: area under the curve 0.811 (95% CI: 0.649; 0.973). A cut-off value of 15.55 ng/mL corresponded to a sensitivity of 70.0% (34.8%; 93.3%), a specificity of 85.7% (67.3%; 96.0%), an accuracy of 81.6% (65 .7%; 92.3%), PPV 63.6% (39.3%; 82.5%), NPV 88.9% (75.4%; 95.4%).
CONCLUSION: Rates of short-term and long-term remission after endoscopic transsphenoidal adenomectomy in our cohort is 79,5% и 61,4%, respectively, and is comparable with literature data for expert pituitary centers. Preoperative GH shows potential value in predicting the long-term remission of acromegaly, but further studies in a larger sample are needed to obtain more accurate cut-off values.
Oncoendocrinology
BACKGROUND: Adrenocortical cancer (ACC) is an orphan malignant tumor of the adrenal cortex with a predominantly poor prognosis and an aggressive clinical course. Nowadays, mitotane is a non-alternative drug in the treatment of ACC. The search for prognostic parameters that determine the sensitivity of ACC to ongoing treatment is currently an urgent task. Expression levels of the large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase M1 (RRM1), cytochrome P450 2W1 (CYP2W1), and sterol- O-acyltransferase-1 (SOAT1) are considered as potential predictors of response to mitotane therapy.
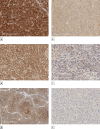
AIM: To assess the immunohistochemical expression of RRM1, CYP2W1 and SOAT1 in ACC as markers of clinical outcomes and response to the therapy with mitotane.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included 62 patients older than 17 years of age with a diagnosis of ACC confirmed histologically and immunohistochemically. Mitotane therapy was initiated in 29 patients in the postoperative period, 33 patients were under dynamic observation without concomitant drug treatment. Antibodies to RRM1, CYP2W1, SOAT1 were used diluted in accordance with recommendations of firms-manufacturers for immunohistochemical detection. RESULTS: In the group of patients with low and moderate RRM1, CYP2W1 and SOAT1 immunoreactivity in the tumor and no antitumor therapy, a better DFS was noted (p=0.037, p=0.020 and p=0.001, respectively) compared to the group of patients receiving mitotane therapy at this level of marker expression. With high immunoreactivity of the markers, no statistically significant differences in DFS were found.
CONCLUSION: Consistent with the findings in our study, low expression of RRM1, CYP2W1 and SOAT1 was associated with worse DFS with antitumor therapy. The results of the work indicate the need to assess the levels of immunoreactivity of these markers in patients with ACC before starting treatment with mitotane in order to predict the efficiency of therapy.
Bones & Adipose tissues diseases
BACKGROUND. There is enough evidence of the negative impact of excess weight on the formation and progression of res piratory pathology. Given the continuing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, it is relevant to determine the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and the clinical features of the novel coronavirus infection (NCI).
AIM. To study the effect of BMI on the course of the acute SARS-COV-2 infection and the post-covid period.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. AKTIV and AKTIV 2 are multicenter non-interventional real-world registers. The АКТИВ registry (n=6396) includes non-overlapping outpatient and inpatient arms with 6 visits in each. The АКТИВ 2 registry (n=2968) collected the data of hospitalized patients and included 3 visits. All subjects were divided into 3 groups: not overweight
(n=2139), overweight (n=2931) and obese (n=2666).
RESULTS. A higher BMI was significantly associated with a more severe course of the infection in the form of acute kidney injury (p=0.018), cytokine storm (p<0.001), serum C-reactive protein over 100 mg/l (p<0.001), and the need for targeted therapy (p<0.001) in the hospitalized patients. Obesity increased the odds of myocarditis by 1,84 times (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1,13–3,00) and the need for anticytokine therapy by 1,7 times (95% CI: 1,30–2,30).
The patients with the 1st and 2nd degree obesity, undergoing the inpatient treatment, tended to have a higher probability of a mortality rate. While in case of morbid obesity patients this tendency is the most significant (odds ratio — 1,78; 95% CI: 1,13-2,70). At the same time, the patients whose chronical diseases first appeared after the convalescence period, and those who had certain complaints missing before SARS-CoV-2 infection, more often had BMI of more than 30 kg/m2 (p<0,001).
Additionally, the odds of death increased by 2,23 times (95% CI: 1,05-4,72) within 3 months after recovery in obese people over the age of 60 years
CONCLUSION. Overweight and/or obesity is a significant risk factor for severe course of the new coronavirus infection and the associated cardiovascular and kidney damage Overweight people and patients with the 1st and 2nd degree obesity tend to have a high risk of death of SARS-CoV-2 infection in both acute and post-covid periods. On top of that, in case of morbid obesity patients this tendency is statistically significant. Normalization of body weight is a strategic objective of modern medicine and can contribute to prevention of respiratory conditions, severe course and complications of the new coronavirus infection.
Pediatric Endocrinology
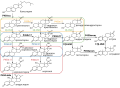
BACKGROUND: Adrenocortical adenomas are often followed with steroid hormones hyperproduction, and therefore determination of their concentration plays an important role in the differential diagnosis of adrenal diseases. Steroid profiling by tandem mass spectrometry is one of the main diagnostic methods in steroidogenesis characterization. Currently plasma and urinary steroid profiling is of particular interest in differential diagnosis and subtyping patients with adrenocortical adenomas.
AIM: Steroid profiling of pediatric patients with adrenal diseases (incidentalomas, ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma, ACTH-independent Cushing syndrome, premature adrenarche).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We conducted a retrospective analysis of steroid profile of 41 pediatric patients with adrenal diseases who were observed between 2005 and 2020 at the Endocrinology Research Centre.
RESULTS: All patients were divided into groups due to diagnosis: with ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma [n=7], ACTH-independent Cushing syndrome (autonomous cortisol secretion by an adrenal adenoma) [n=4], with incidentaloma [n=7] and premature adrenarche [n=23]. In group of patients with ACTH-independent Cushing syndrome identified statistically significant higher levels of 11-deoxycortisol (р=0, 0035) and significant lower levels of 17-hydroxypregnenolone (р=0, 0026) and DHEA (р=0, 0047) compared to other groups. Statistically significant differences in steroid profiles between other groups were not identified.
CONCLUSION: Results of our study steroid profiling can be used as additional differential diagnosis method in patients with adrenocortical adenomas with or without hormonal hyperproduction (ACTH-independent Cushing syndrome and incidentaloma). Further studies are needed to identify steroid markers for subtyping pediatric adrenal diseases.
Often transfusions red blood cells in patients with hereditary anemias lead to iron overload, that can cause endocrine complications, such as growth retardation, hypothyroidism, hypogonadism, and disorders of carbohydrate metabolism.
Clinical case 1. A boy with transfusion-dependent (TD) Diamond-Blackfan anemia at 16.3 years presented with impaired fasting glucose, growth hormone (GH) deficiency, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; GH therapy was initiated. At the age of 16.8 years old secondary hypothyroidism, secondary hypocorticism and diabetes mellitus were diagnosed. At 17.2 years continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) detected glucose elevations up to 11.7 mmol/l. Therapy with GH and testosterone ethers was continued; levothyroxine and cortef were stopped by patient. At 17.9 years height was 163 cm; no data supporting hypothyroidism nor hypocorticism; glycaemia within goal range.
Clinical case 2. A girl with TD beta-thalassemia major at the age of 11.5 years presented with GH deficiency; GH therapy has been conducted from 12.8 to 15.3 years of age. At 13.8 years retardation of pubertal development was diagnosed. At 15.0 hyperglycemia 7.2 mmol/l was detected; normal results of oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were observed; glycemia elevations were up to 9.5 mmol/l according to CGM data. At 16.0 height was 152 cm; because of pubertal development arrest hormone replacement therapy was prescribed.
CONCLUSION. Growth, pubertal and carbohydrate metabolism disorders were diagnosed in patients with TD hereditary anemias, that confirms the necessity of regularly endocrine investigation. To detect impairment of carbohydrate metabolism investigation of fasting blood glucose, OGTT, and CGM is recommended; glycated hemoglobin measurement is not considered reasonable.
The prevalence of obesity and related metabolic disorders in children and adolescents in the Russian Federation is steadily increasing, which requires healthcare professionals to search for new methods of treatment and prevention. The treatment of childhood obesity should be based on a comprehensive approach, including diet therapy, increased physical activity, behavioral therapy and psychological support. To increase the effectiveness of the formation of new eating habits and proper eating behavior, as well as to increase the adherence of children and adolescents to treatment, drug therapy of obesity is used, aimed primarily at reducing appetite. Considering the efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide 1 analog (Liraglutide) in adolescents, as well as a small number of gastrointestinal side effects, this drug is promising in the complex treatment of childhood obesity. This review presents an analysis of the literature on non-medicated and drug-based methods of treatment of childhood obesity.
Reproductive Endocrinology
Today most adolescents have their first sexual experience at the age of 15–19. However, only 44% of girls and young women (15–24 years old) report about contraception at that moment. A decision on pregnancy in adolescence is a difficult choice and any scenario may cause serious medical and social problems. Complications after an artificial abortion have a negative impact on a woman’s fertility. Diabetes mellitus type 1 and arterial hypertension accompanied with obesity within the metabolic syndrome are defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as diseases, which increase risk of an unplanned pregnancy. The article consoders problems of interaction of a doctor and a teenage girl with endocrinopathy, when discussing her sexual health, the analysis of the literature reflecting the influence of contraception on the course of the underlying pathology is presented. The authors formed a list of drugs acceptable for use in diabetes and obesity based on assessment of risks and preferences from the use of different methods of fertility control. The work contains information about the procedure of starting contraception, the rules of future dynamic monitoring of the patient.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s disease. There is evidence that PD has a wider prevalence among men, which indicates the existing role of sex hormones in the pathogenesis of the disease. The article presents an overview of studies devoted to the study of sex differences in the incidence and symptoms of PD. Drug therapy with androgens, androgen precursors, antiandrogens and drugs that modify androgen metabolism is available for the treatment of various endocrine conditions, having translational significance for PD, but none of these drugs has yet shown sufficient effectiveness. Although PD has now been proven to be more common in men than in women, androgens do not always have any effect on the symptoms or progression of the disease. 5α-reductase inhibitors have shown neuroprotective and anti-dyskinetic activity and need further investigation. Despite the fact that the neuroprotective effect of dutasteride was observed only before damage to DA neurons, the absence of a negative effect makes it an attractive drug for use in patients with PD due to its anti-dyskinetic properties.
Studies of recent decades show a steady increase in the average life expectancy of a person, and women in particular. The World Health Organization predicts a four-fold increase in the number of women over 70 by 2030, and many of them over the age of 45 may face menopausal problems. Menopause is a physiological state in a woman’s life, during which, against the background of age-related changes, there is a gradual decrease and shutdown of ovarian function and the cessation of estrogen production. Genitourinary syndrome occurs in every third woman in this period. Estriol is the main estrogen that specifically addresses problems associated with estrogen deficiency: dyspareunia, dryness and itching in the vagina and lower genitourinary tract, urinary incontinence, moderate urinary incontinence, and recurrent vulvovaginitis and cystitis. Vulvovaginal dystrophy in women of the older age group is a multidisciplinary problem at the intersection of gynecology, urology and dermatology, which can and should be solved to prevent more severe gynecological and urological pathologies.
Short Messages
On September 30, 2022, a meeting of the interdisciplinary expert council “Prevention and treatment of obesity. How to Achieve a Healthy Metabolic Balance. To reduce the social and economic burden of obesity and its consequences in the Russian Federation, it is necessary to introduce socially significant initiatives to prevent obesity and increase its detection rate, as well as to update modern approaches to the treatment of this chronic disease, taking into account its multifactorial pathogenesis, comorbidity, risk of complications and patient disability. Based on the results of the scientific reports and discussions held during the expert council, the experts made decisions on a further plan within the framework of socially significant initiatives for the prevention of obesity
Obituary
On January 1, 2023, at the age of 59, the head of the Diabetes Prediction and Innovation Department of the Diabetes Institute of the State Scientific Center-FGBU «NMITs of Endocrinology» of the Ministry of Health of Russia, the president of the All-Russian Public Organization of the Disabled «Russian Diabetes Association» endocrinologist and diabetologist, doctor of medical sciences, died suddenly Professor Mayorov Alexander Yurievich.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2308-1430 (Online)










































.jpg)


