
Since 1936 the “Problems of Endocrinology” (or “Problemi Endocrinologii”) Journal has been publishing timely articles, balancing both clinical and experimental research, case reports, reviews and lectures on pressing problems of endocrinology.
The Journal pays special attention to the most relevant issues of endocrinology: to chemical structure, biosynthesis and metabolism of hormones, the mechanism of their action at cellular and molecular level; patogenesis and to clinic of the endocrine diseases, new methods of their diagnostics and treatment.
The Journal:
- features original national and foreign research articles, reflecting world endocrinology development;
- issues thematic editions on specific areas;
- publishes chronicle of major international congress sessions and workshops on endocrinology, as well as state-of-the-art guidelines;
- is intended for scientists, endocrinologists, diabetologists and specialists of allied trade, general practitioners, family physicians and pediatrics.
The “Problems of Endocrinology” Journal is included into the “List of leading scientific journals under review, where principal data of applicants for scientific degree has to be published”, as decreed by State Commission for Academic Degrees and Titles in Bulletin №2 of 2003 and revised in 2010.
The journal is indexing in the following international databases and directory editions: SCIENCE INDEX (Russian Index of Scientific Citing), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, BIOSIS Previews, Google Scholar. Since 1955 the journal is the member of the European association of scientific editors (EASE).
The journal is registered by Council of ministers of the USSR, the State committee USSR on the press – registration No. 1133 of 07.12.1990.
The journal is registered by Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Telecom, Information Technologies and Mass Communications – registration № ФС77-36291 from 13.05.2009г.
Current issue
Clinical endocrinology
Oncoendocrinology
Pediatric Endocrinology
Reproductive Endocrinology
Announcements
2024-11-02
ЖУРНАЛ "ПРОБЛЕМЫ ЭНДОКРИНОЛОГИИ" ВХОДИТ В ПЕРЕЧЕНЬ ОТЕЧЕСТВЕННЫХ ИЗДАНИЙ ВАК
Журнал «Проблемы эндокринологии» входит в Перечень отечественных изданий Высшей аттестационной комиссии, в котором должны быть опубликованы основные научные результаты диссертаций на соискание ученой степени кандидата и доктора наук.
Согласно Приказу Министерства образования и науки РФ от 12 декабря 2016 г. N 1586, "Об утверждении правил формирования перечня рецензируемых научных изданий, в которых должны быть опубликованы основные научные результаты диссертаций..." издания, текущие номера которых или их переводные версии входят хотя бы в одну из международных реферативных баз данных и систем цитирования Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, MathSciNet, zbMATH, Chemical Abstracts, Springer или GeoRef считаются включенными в перечень по отраслям науки, соответствующим их профилю (Пункт 5 Приложения №1).
Таким образом, хотя журнал "Проблемы эндокринологии" отсутствует в списке "Перечень рецензируемых научных изданий, в которых должны быть опубликованы основные научные результаты диссертаций на соискание ученой степени кандидата наук, на соискание ученой степени доктора наук", он считается автоматически входящим в Перечень на основании вышеупомянутого Приказа.
Документальным подкреплением этому служит документ Справочная информация об отечественных изданиях, которые входят в международные реферативные базы данных и системы цитирования, в котором журнал "Сахарный диабет" размещен под номером 972.
2024-11-02
"ПРОБЛЕМЫ ЭНДОКРИНОЛОГИИ" ОТНОСИТСЯ К КАТЕГОРИИ ИЗДАНИЙ К1 (ВАК)
Согласно Письму Минобрнауки №02-1198 от 6 декабря 2022 г. "О перечне рецензируемых научных изданий", журналы, входящие в международные базы данных Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, MathSciNet, zbMATH, Chemical Abstracts, Springer или GeoRef и перечень журналов RSCI, приравниваются к изданиям категории К1.
| More Announcements... |

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).



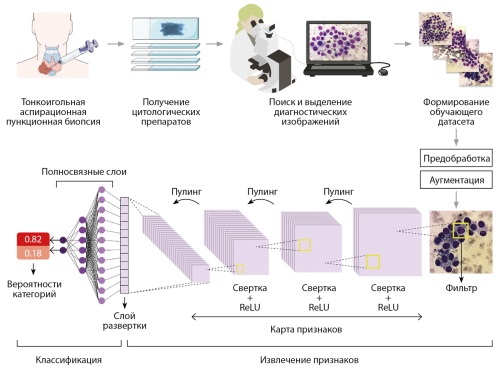
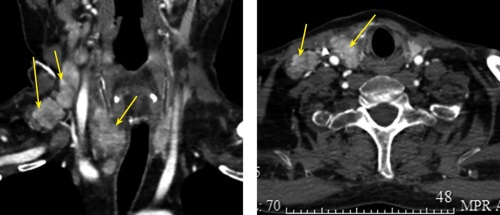
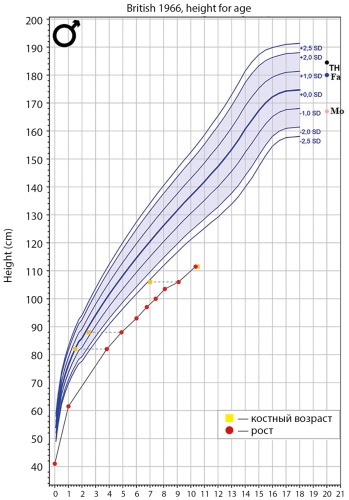
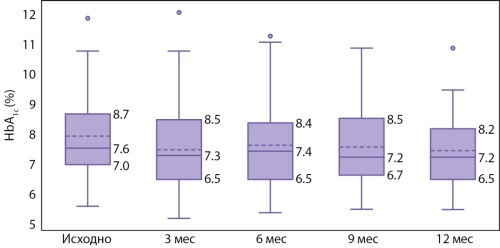
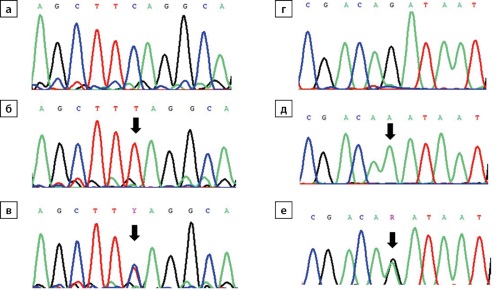
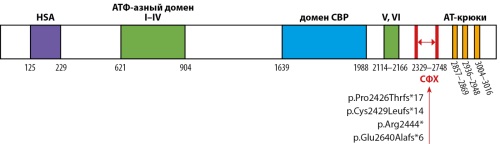
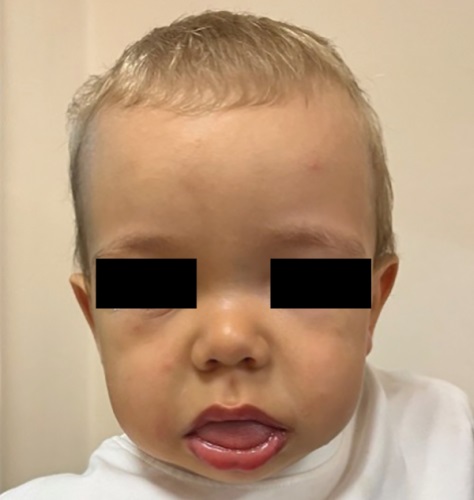




































.jpg)


