Clinical endocrinology
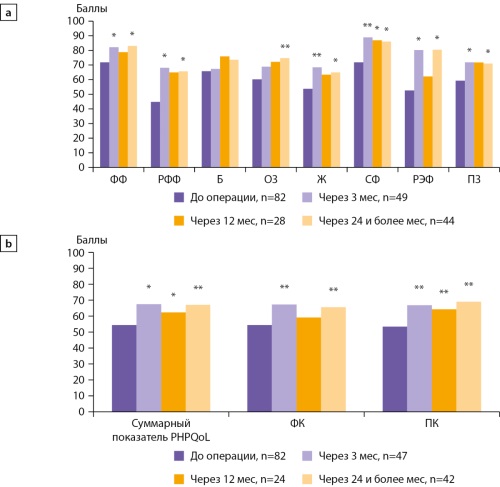
BACKGROUND: For a comprehensive assessment of the effect of surgery in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) it sounds reasonable to evaluate quality of life (QoL) and symptoms in PHPT patients at long-term after parathyroidectomy (PTE). The purpose of this study was to study the quality of life of patients with PHPT before and at different times after PTE and to determine the factors associated with its improvement after surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: During prospective observational study, patients filled out QoL questionnaires before, 3, 12, 24 months or more after surgery. Statistical analysis was performed using the Student’s t-test, the Mann-Whitney U-test, χ2 criterion, the method of generalized estimating equations (GEE) and binary logistic regression. The differences were considered significant at the level of p<0.05.
RESULTS: The study included 82 patients (mean age 53,7 years, 95% female) with symptomatic (73%) and asymptomatic (27%) PHPT. Median follow–up duration was 20 (3–31) months. At 3 months after PTE, there was a significant increase in QoL for all scales of the generic SF-36 questionnaire, except for the pain scale, compared with their preoperative values, followed by the preservation of positive changes at long term after surgery (GEE, p<0.05). At the long term after surgery, scores for all SF-36 scales, except for role physical functioning (p=0.011), became similar with the ones in comparison group adjusted to patients by gender and age (n=60, 52.5±9.2 years, 95% were women). An independent predictor of significant improvement in QoL after PTE was the preoperative level of the mental component according to the PHPQoL questionnaire (p=0.001) — the lower its level, the greater the probability of significant improvement in QoL according to the total PHPQoL index after surgery (OR=0.924, p=0.004).
CONCLUSION. PTE is accompanied by significant improvement in QoL and regression of symptoms in patients with PHPT at long term follow-up after surgery. An independent predictor of significant QoL improvement after PTE is the preoperative level of the psychological component of QoL.
BACKGROUND: Insulinoma is a neuroendocrine tumor, the main manifestation of which is hypoglycemia. However, the symptoms of hypoglycemia can be non-specific for a long time, especially outside provocative conditions, and quite often the tumor manifests from a life-threatening condition — hypoglycemic coma. In this regard, timely laboratory diagnosis of insulinoma and determination of its aggressive course is one of the priorities in modern researches.
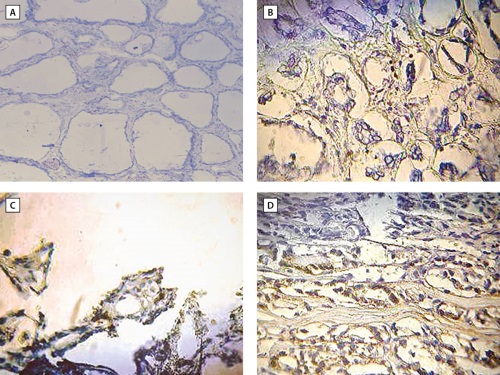
AIM: Search for new immunohistochemical (IHC) and circulating markers (CM) of insulinoma, including its aggressive course.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The patients examined at the Endocrinology Research Centre in the period 2017–2022 and operated on for an insulin-producing tumor were included. Before surgery and 2–12 months after it, blood sampling was performed with the determination of targeted marker proteins. Some patients underwent an extended IHC examination of the tumor, surrounding tissue and islets of Langerhans with primary antibodies to target marker proteins with an assessment of the degree of their expression. To determine the aggressive course of the tumor, the degree of malignancy (Grade), the number of tumors and signs of recurrence were characterized.
RESULTS: Based on the analysis of literature and pathogenetic characteristics of insulinoma, the following candidates for targeted marker proteins were selected: cocaine and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART), chromogranin B (CrB), neuroendocrine secretory protein 55 (NESP55), glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1), arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (AA-NAT), melatonin, and, exclusively for IHC research, protein D52 (TPD52), as well as receptors for glucagon-like peptide-1 (rGLP1) and melatonin (MTNR1b). 41 patients were included in the study, of which 10 patients underwent an extended IHC study. In patients with both aggressive and non-aggressive insulinoma after surgical treatment, CM levels did not change significantly and in individual patients they could both increase and decrease, including those patients with the expression of the corresponding marker in tumor tissue. It was shown that CART was expressed only in the tumor (in 4/10 of cases), while MTNR1b and rGLP1 were expressed in the tumor (in 6/10 and 10/10, respectively) and the islets of Langerhans (in 5/9 and 9/9, respectively). The association of marker expression with the aggressiveness of the course of insulinoma has not been revealed.
CONCLUSION. The markers CART, MTNR1b and rGLP1 are of primary interest for further study in a larger sample of patients with insulinoma. Other markers (TPD52, XgB, NESP55, melatonin, AA-NAT) have not been shown to be associated with an insulin-producing tumor, therefore they are not promising for future researches. At the same time, it is necessary to continue research aimed at finding new both circulating and IHC markers in order to early diagnose the manifestation of the disease and its recurrence, and more accurately determine the malignant and proliferative potential of the tumor.
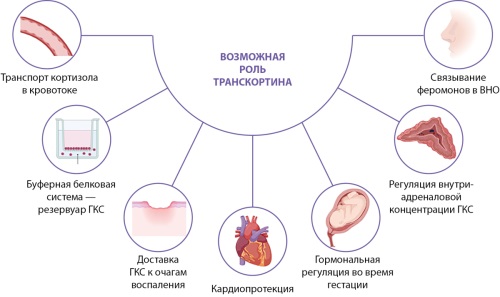
Steroid hormones take an active part in a whole complex of physiological processes that are fundamental for the normal development and functioning of the human body. In the bloodstream steroid hormones are bind with specific transport proteins, in particular with transcortin. The matter of changes in hormone-protein complex in various conditions were actively studied in the second half of the twentieth century, but currently this issue has been taken a back seat by the development of high-precision diagnostic methods of steroid hormones determining. This literature review presents accumulated data on the physicochemical properties of transcortin, genetic factors affecting its synthesis and secretion. Published data on its physiological significance in the human body are analyzed in detail within the framework of not only the “free hormone” hypothesis, but also the reservoir hypothesis. Research results have shown that the synthesis of transcortin has been detected in some extrahepatic tissues, including the adrenal glands, however, its role is unknown.
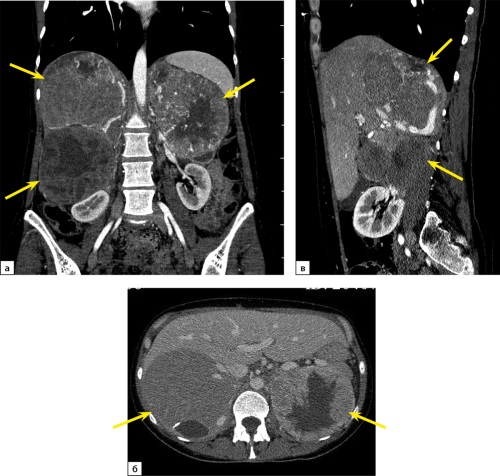
Pheochromocytoma (PHEO) currently is considered to be malignant due to metastatic potential. One of the most common familial forms of PHEO is multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (MEN) type 2. The penetrance of PHEO in MEN2 syndrome is up to 50% of cases. It may be one- or two-sided, but metastases occur extremely rare. The fact that in majority of cases of MEN2 syndrome the source of distant metastases is medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) complicates differential diagnosis in case of PHEO metastasis.
Isolated cases of PHEO with metastases to the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones, brain in MEN2 patients were described. In the available literature, we have found a description of 31 cases of metastatic PHEO in MEN2 syndrome. The available data of those cases is presented as a table in the article.
We present a description of a 40-year-old woman with MEN2A syndrome (mutation of the RET proto-oncogene p.Cys634Tyr), with a history of twice-performed surgical treatment of MTC, with daily crises of arterial hypertension accompanied by vegetative symptoms, with a giant bilateral PHEO (up to 200 m on the right and up to 150 mm on the left) with synchronous large metastasis (up to 50 mm) into the pubic bone with the destruction. The patient underwent several surgeries: bilateral adrenalectomy, then a bilateral revision of the neck, removal of the right upper and right lower parathyroid glands, residual thyroid tissue, then resection of the right pubic bone with a tumor.
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body. About 99% of calcium is deposited in the bones in the form of hydroxyapatite and only 1% is located in the intracellular and extracellular fluid. Ionized calcium, which makes up about 50% of the total amount of circulating calcium, is biologically active; the remaining percentage is bound to plasma proteins (40%, of which albumin accounts for 90%, and globulins for 10%), or is in complex with anions (10%) such as citrate, lactate, bicarbonate, phosphate. Hypo- and hypercalcemia are common conditions treated by physicians of various specialities. Primary hyperparathyroidism and malignant tumors are the most common causes of hypercalcemia, whereas hypocalcemia is most often caused by hypoparathyroidism, malabsorption, vitamin D deficiency or chronic kidney disease. The interpretation of blood calcium concentration results affects the correct diagnosis, the need for further examination, and the choice of treatment. Concentration of ionized calcium is considered a more accurate indicator of the true status of calcemia compared to the concentration of total calcium, but its measurement is difficult due to strict preanalytical and analytical requirements. In the mid-1970s, calcium adjustment equations appeared, which are widely used today. However, some studies have expressed doubts about the sufficient reliability and sensitivity of the corresponding adjustment formulas. The diagnostic accuracy of widely used correction formulas in some clinical situations is lower than the diagnostic accuracy of uncorrected total calcium. The review discusses the history of the formulas for correcting total calcium for albumin, the factors influencing the result of correction, as well as its suitability in various conditions.
Oncoendocrinology
BACKGROUND. KI-67 (MKI-67 in humans) is a protein able to bind to DNA which contributes to cell growth and cell proliferation. KI-67 is currently considered as a biomarker that is widely utilized as prognostic indicator for evaluating cell proliferation, diagnosing diseases, and conducting research. Several different kinds of cancer have high Ki-67 expression, which simplifying the choice of treatment for individuals with various cancer types.
AIM. The objective was to evaluate the expression of KI67 in patients suffering papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) also the association between patients age and gender and KI67 expression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. To undertake an in-depth investigation of KI67 in malignant and normal tissues, we used thyroid tissue sections to analyze KI67 expression in 70 samples, 50 different PTC (44 female and 6 male), and 20 normal types (10 for each gender). Each group’s average age is between 20 and 60.
RESULTS. The analysis of the data revealed a substantial difference in the expression of ki67 between the patients and control groups. Ki67 expression and either gender or age did not significantly correlate.
CONCLUSION. This study suggest that KI67 may be a crucial marker for assessing the aggressiveness of tumors and inflammatory diseases.
Bones & Adipose tissues diseases
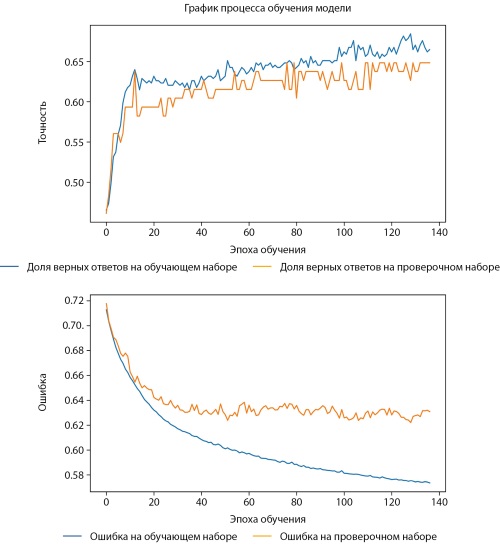
BACKGROUND: Osteoporosis is a common age-related disease with disabling consequences, the early diagnosis of which is difficult due to its long and hidden course, which often leads to diagnosis only after a fracture. In this regard, great expectations are placed on advanced developments in machine learning technologies aimed at predicting osteoporosis at an early stage of development, including the use of large data sets containing information on genetic and clinical predictors of the disease. Nevertheless, the inclusion of DNA markers in prediction models is fraught with a number of difficulties due to the complex polygenic and heterogeneous nature of the disease. Currently, the predictive power of neural network models is insufficient for their incorporation into modern osteoporosis diagnostic protocols. Studies in this area are sporadic, but are widely demanded, as their results are of great importance for preventive medicine. This leads to the need to search for the most effective machine learning approaches and optimise the selection of genetic markers as input parameters to neural network models.
AIM: to evaluate the effectiveness of machine learning and neural network analysis to develop predictive risk models for osteoporosis based on clinical predictors and genetic markers of osteoporetic fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The predictive models were trained using a database of genotyping and clinical characteristics of 701 women and 501 men living in the Volga-Ural region of Russia. Anthropometric parameters, data on gender, bone mineral density level, and the results of genotyping of 152 polymorphic loci of candidate genes and replication loci of the GEFOS consortium’s full genome-wide association search were included as input parameters.
RESULTS: It was found that the model for predicting low bone mineral density, including 6 polymorphic variants of the OPG gene (rs2073618, rs2073617, rs7844539, rs3102735, rs3134069) and 5 polymorphic variants of microRNA binding sites in the mRNA of genes involved in bone metabolism (COL11A1 — rs1031820, FGF2 — rs6854081, miR-146 — rs2910164, ZNF239 — rs10793442, SPARC — rs1054204 and VDR — rs11540149) (AUC=0.81 for men and AUC=0.82 for women).
CONCLUSION: The results confirm the promising application of machine learning to predict the risk of osteoporosis at the preclinical stage of the disease based on the analysis of clinical and genetic factors.
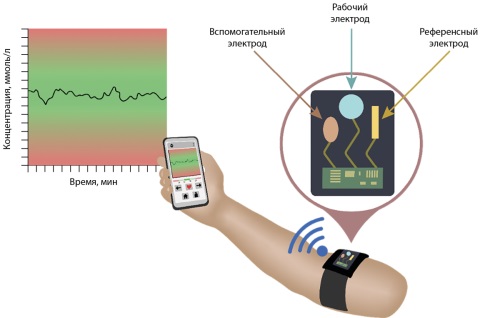
Disorders of calcium and phosphorus metabolism can cause severe complications that require changing of therapeutic strategies and a long treatment in a hospital. The prevalence of diseases accompanied by calcium metabolism disorders varies from low to moderate. For example, primary hyperparathyroidism, as one of the most common causes of pathological changes in calcium metabolism due to parathyroid hormone hypersecretion, occurs with a frequency of 85 to 233 cases per 100 thousand people. In countries where blood calcium measurements are not routinely carried out, this disease and similar conditions are diagnosed less frequently, and at later stages, with a predominance of manifest and complicated forms. However, calcium metabolism disorders require timely detection and correction in order to prevent complications. At the same time, in a number of clinical situations, standard laboratory analysis is not the optimal diagnostic option due to the duration and complexity of its implementation. In particular, the development of acute hyper- and hypocalcemia requires faster obtaining of blood test results. It is promising to apply technologies allowing to quick assess the current level of calcium directly at a doctor’s appointment especially in cases of drug doses adjustment for patients with chronic disorders of calcium metabolism. In this regard, when long-term monitoring of calcemia is required or in emergency situations, the potential benefit can be obtained by using portable Point-of-Care (POC) devices or wearable biosensors. This review examines the clinical and methodological aspects of monitoring calcium levels, their capabilities and practical limitations, and also highlights the prospects for the development and implementation of POC devices and biosensors for ionized calcium.
Pediatric Endocrinology
BACKGROUND: Deficiency of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 (HSD17B3) is a rare variant of 46,XY disorders of sex development (DSD).
AIM: To give clinical, hormonal and molecular genetic characteristics of cases of 46,XY DSD associated with variants in the HSD17B3 gene.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included 310 patients with 46,XY DSD for the period from 2015 to 2019. The patients underwent a comprehensive examination, including a study of the steroid profile by high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection, as well as a molecular genetic analysis using NGS.
RESULTS: According to the results of molecular genetic studies, biallelic nucleotide substitutions in the HSD17B3 gene were detected in 13 cases, which accounted for 4.2% of the total number of patients with 46,XY DSD. All 13 patients with biallelic variants in the HSD17B3 gene were registered as females. The ratio of androstenedione/testosterone concentrations in the blood in this group ranged from 1.4 to 8.9. 2 variants in the HSD17B3 gene were found in several patients: c.277+4A>T (on 6 chromosomes) and c.729_735del:p.V243fs (on 9 chromosomes). 4 novel variants have been identified. Monoallelic nucleotide substitutions in the HSD17B3 gene were detected in 7 cases, which accounted for 2.3% of the total number of patients with 46,XY DSD. External genitalia in this group corresponded to Prader stages 3–4. In 1 patient, a pathogenic variant c.277+4A>T was detected in the HSD17B3 gene, in other cases variants with uncertain significance were detected.
CONCLUSION: In the structure of 46,XY DSD, patients with biallelic variants in the HSD17B3 gene were identified in 4.2% of cases, with monoallelic variants — in 2.3% of cases. 4 novel variants were found in the HSD17B3 gene.
BACKGROUND: Childhood obesity and the rate of its spread is a serious threat to the reproductive health of the nation, especially among boys, being a background for delaying sexual development and further disrupting fertility.
AIM: To study the peculiarities of the ratio of the level of leptin and a number of toxic and essential chemical trace elements in biological environments in adolescent boys aged 13–14 years with obesity and delayed sexual development.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Three groups of adolescents aged 13–14 years were studied and formed: the main ones — with constitutional exogenous obesity of 1–2 degrees (1–20 boys without secondary signs of puberty; 2 — 24 boys with 2–4 stages of puberty according to Tanner) and comparisons (3 — 15 boys with normal body weight and without deviations in puberty). The level of lead, zinc, selenium, chromium and manganese in the morning urine was determined by the absorption method; in the blood serum — leptin, by the method of enzyme immunoassay. Statistical analysis of the data was carried out in the MeoCape 11.4.2 Statistica environment, nonparametric Spearman correlation analysis and calculation of the Student’s t-test for independent samples, the reliability of the results at p< 0.05.
RESULTS: It was found that adolescents with obesity are characterized by a certain shift in the content of toxic and essential trace elements, the vector of which is shifted towards the predominance of levels of toxic chemical elements, in particular, ead, and a decrease in essential toxic elements, such as zinc, selenium, chromium and manganese. However, a more pronounced shift in the values in the imbalance of trace elements already violates not only the metabolic processes in the body of adolescent children, but also leads to a violation of puberty - to a delay in sexual development. CONCLUSION: In the body of adolescent boys with obesity and delayed sexual development, the processes of oxidative stress, tissue hypoxia are progressing against the background of excess leptin, accumulation of heavy metals and deficiency of essential trace elements. Less pronounced shifts in the content of leptin and trace elements in adolescent boys are determined by a failure in neuroendocrine regulation, but does not affect the level of puberty. The homeostasis of the hormonal-microelement composition ensures the harmonious development of adolescent boys.
BACKGROUND: Differential diagnosis of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) and constitutional delay of puberty (CDP) is extremely important since with the latter puberty begins and completes without any medical intervention and in the case of HH puberty does not occur or is incomplete. Failure to start treatment on time leads to medical and psychosocial maladjustment of the patient.
AIM: Development of a method for differential diagnosis of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and constitutional delay of puberty in boys 13.5–17 years old by scoring the levels of LH, FSH, testosterone and inhibin B.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study group was formed by adolescent men 13.5–17 years old with delayed puberty including all observations. Anamnesis, stage of puberty, testicular volume were assessed; serum levels of LH, FSH, testosterone (T) were determined by chemiluminescent analysis and inhibin B, AMH by ELISA. Stimulation tests were performed with triptorelin and human chorionic gonadotropin (3 days). Patients were followed up for 6–24 months.
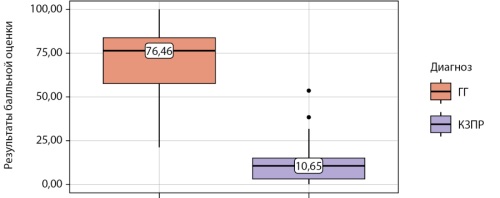
RESULTS: The study included adolescent men at the age of 13.5–17 years with delayed puberty: 56 for the purpose of development a method of differential diagnosis, 30 for its control (control group). We`ve created a method that allows differentiate HH and CDP. Through the ROC-analysis the most sensitive and specific HH markers were identified. The basal levels of LH, FSH, T, and inhibin B were selected as most available for outpatient testing. Based on the results of our own research and scientific data we selected ranges of values and rated LH, FSH, T and inhibin B depending on them (marks). Then we assigned the coefficients (k) for each hormone. Scores were calculated by multiplying the marks by k then summed and normalized to the maximum amount the patient could get. To increase the accuracy of diagnosis an age coefficient was introduced. The result of the calculation was the result of the scoring (S). S for CDP (10.65 [3.13–14.91]) differed significantly from that for HH (76.46 [57.79–83.74]) (p< 0.001). Diagnoses based on S (<21.16 and ≥55.07) in the control group were confirmed by follow up data in 97% cases. An algorithm for the differential diagnosis of HH and CDP by using S has been developed.
CONCLUSION: The result of scoring of LH, FSH, testosterone, inhibin B levels ≥55.07 makes it possible to diagnose hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, < 21.16 — constitutional delay of puberty with a high probability. In the case of score ≥21.16 but < 55.07, calculation of the inhibin B/AMH ratio and/or stimulation tests are required.
Reproductive Endocrinology
Amenorrhea is a common symptom of a whole range of nosologies among women of reproductive age, which can accompany any endocrinopathy in the stage of decompensation. In all the diversity of various links in the pathogenesis of reproductive disorders, the problem of immunopathology remains a little aside, however, the significance of these disorders is underestimated. This publication provides an overview of immune system abnormalities in a women with amenorrhea. As is known, in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), one of the clinical manifestations is amenorrhea. On the one hand, these nosologies differ significantly from each other in etiology, pathogenesis and approaches to therapy, and on the other hand, they have a common similarity, manifested by immunological disorders. The article provides information about the immune status of patients with PCOS and POI. Works devoted to various disorders in the immune system, pathologies of humoral and cellular immunity, which in the future may serve as the key to the development of new and non-standard methods of treating such socially significant diseases, are analyzed. Literature search was carried out in national (eLibrary, CyberLeninka.ru) and international (PubMed, Cochrane Library) databases in Russian and English. The choice of sources was prioritized for the period from 2018 to 2024.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2308-1430 (Online)








































.jpg)


