Editorial notice
Obesity is a consequence of chronic energy imbalance when energy intake constantly exceeds expenditure, which leads to excess white adipose tissue accumulation. Effective treatment of obesity requires accurate measure of calories intake and expenditure, as well as related behavior to understand how energy homeostasis is regulated and evaluate the effectiveness of the measures taken. The greatest interest is to study features of energy metabolism in various forms of obesity. It is necessary to create an evidence-based, personalized approach to diet therapy and to increase the effectiveness of weight loss measures. Modern studies have shown that the use of indirect calorimetry in obesity treatment programs leads to greater weight loss compared to traditional diet therapy planning based on calculated formulas.
Clinical endocrinology
BACKGROUND: The combination of primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) with anemia was first described in 1931. It remains unclear whether PHPT is the direct cause of anemia, or it develops due to PHPT’s complications. The frequency of PHPT-associated anemia in the Russian population is unknown.
AIM: To assess the prevalence of anemia in patients with PHPT admitted to the Department of Parathyroid Glands Pathology in the Endocrinology Research Centre from January 2017 to August 2020.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included patients with PHPT over 18 years old. A single-center observational one-stage one-sample uncontrolled study was carried out. We analyzed laboratory and instrumental data obtained during inpatient examination in accordance with the standards of medical care. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistica 13 (StatSoft, USA) and SPSS (IBM, USA) software packages.
RESULTS: The study included 327 patients with PHPT, 28 (9%) men and 299 (91%) women. The median age was 59 years [51; 66]. 26 patients (8%) with anemia were identified. Statistically significant differences between patients with and without anemia were found only in the GFR. Comparison of patients with and without anemia didn’t reveal any significant differences in the incidence of PHPT’s complications.
Significant differences in serum hemoglobin concentration and average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes were revealed between patients with and without vertebrae fractures. In the group of patients without compression fractures these parameters were higher.
In the subgroup of patients with total calcium concentration above 3 mmol/L and PTH above 3 normal values, the incidence of anemia reached 21% (95% CI: 10%; 35%). Within this group we revealed tendencies to higher levels of PTH, ionized calcium and osteocalcin in patients with anemia.
CONCLUSION: In general, there was no correlation between hypercalcemia, the degree of PTH elevation and the presence of anemia in patients with PHPT. However, in the subgroup of patients with severe hypercalcemia, there was a relationship between the concentration of PTH, ionized calcium and the presence of anemia. In patients with PHPT and vertebral fractures, significantly lower concentrations of blood hemoglobin and hemoglobin in erythrocytes were observed.
BACKGROUND: The association between vitamin D deficiency and the severity of COVID-19 is currently being actively discussed around the world.
AIM: The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency and compare it with the incidence rates of SARS-CoV-2 in eight Federal Districts of the Russian Federation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We included 304,564 patients (234,716 women; 77,1%) with serum 25(OH)D levels results performed September 2019 through October 2020.
RESULTS: Only 112,877 people (37.1%) had a normal serum 25(OH)D level, others had a deficiency. Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency was presented with the same frequency in women and men, and no differences were found depending on the geographical location and age in subjects from 18 to 74 years old. However, subjects over 75 years more often had vitamin D deficiency, while subjects under 18 years had normal levels in over 50% cases. In addition, 21,506 patients were tested for SARS-CoV-2 by PCR with further comparison of results with serum 25(OH)D level. The SARS-CoV-2 positivity rate was detected in 3,193 subjects, negative in 18,313. There were no differences in the morbidity in a vitamin D deficiency and a normal level. Thus, 14.8% subjects had positive PCR rates among vitamin D deficiency patients (4,978 tests), 14.9% when 25(OD)D level was from 20 to 30 ng/ml (7,542 tests), 15.0% among those who had 25(OH)D 30- 50 ng/ml (6,622 tests), and 13.9% when vitamin D was more than 50 ng/ml (4,612 tests).
CONCLUSION: There was no association between the COVID-19 incidence and vitamin D status in different regions of Russia. Although the nutrient deficiency persists in all regions and is most often diagnosed in people over 75 years old.
Experimental endocrinology
BACKGROUND: Prolactin-releasing peptide(Prl-RP), in addition to stimulating the production of prolactin, interacts with various parts of the central nervous system, participating in the implementation of many functions that are reflected in behavior.
AIM: The effect of Prl-RP on the anxiety of white Wistar rats was studied since there were no data in the literature on the relationship between Prl-RP and anxiety.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Anxiety was assessed in two tests. In the elevated plus-maze (EPM), the time spent in the open arms and the number of edge reactions were recorded. In the social preference test, the time spent near a stranger, near a familiar individual, and in neutral territory were recorded.
RESULTS: The administration of Prl-RP at a dose of 10-10 M with a volume of 10 µl in each nostril reduced the time spent by the animals in the open arms of the EPM, and the number of edge reactions. For testing the social interaction, animals were pre-selected for high or low levels of anxiety in the EPM. In rats with initially low levels of anxiety, Prl-RP reduced the time spent near a stranger, indicating an increase in anxiety levels. The behavior of rats with initially high levels of anxiety did not change after application of the Prl-RP.
CONCLUSION: The results of our experiments indicate that the intranasal administration of Prl-RP increases the anxiety of rats.
Carbohidrates metabolism disturbancies
Diabetes mellitus and malignant tumors are among the most common and complex diseases. Epidemiological studies have shown a strong relationship between these pathologies. The causality of this relationship has not yet been unambiguously established, but a number of probable biological mechanisms have been proposed to explain it through the effects of hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia on the process of oncogenesis. An important role in this is played by the axis of insulin-like growth factors, their receptors and binding proteins (IGF / IGFR / IGFBP). The review provides data on the structural elements of the insulin / IGF / IGFR / IGFBP signaling axis and their internal relationships in diabetes mellitus and in the development of malignant tumors. Significant changes in the axis that occur during the formation of the diabetic environment prepare the background, which, under certain conditions, can lead to the stimulation or inhibition of tumor development. The considered signaling system, playing a significant role in the physiology of normal cells, often functions as a decisive factor in the survival of tumor cells, providing fine context-dependent regulation of many cellular processes associated with oncogenesis. However, despite many years of in-depth studies of the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and malignant tumors, the molecular mechanisms of the relationship between these pathologies are still largely unclear, and the internal heterogeneity of pathologies complicates research and interpretation of the results, leaving many questions.
Pediatric Endocrinology
More than 30 genes are known to take part in hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis development at the date and role of more than 10 other genes is studied. Despite it about 50% of isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism cases still have no molecular genetic explanation.
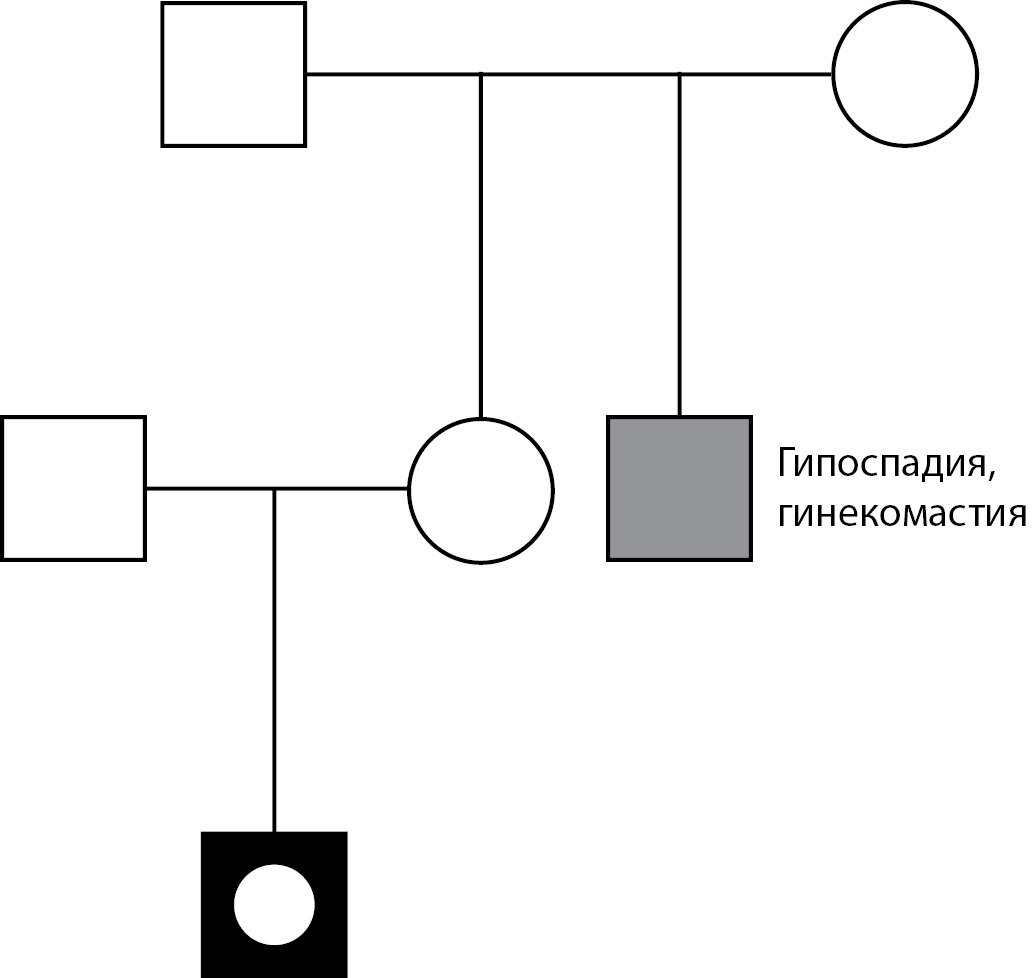
A number of specific associations between iHH and different not-reproductive manifestations called syndromic forms are distinguished in general group of iHH. For example, the combination of Kalmann syndrome with sensorineural hearing loss is known as manifestation for defects of some genes encoding factors of neuronal migration; in patients with this phenotype CHD7, SOX10 genes defects are most frequent. However, defects in the genes of neuronal migration factors are characterized by a wide variability of phenotype, which is explained by the epigenetic mechanisms influence. Carriers of the mutation within the same family may lack some non-reproductive manifestations as well as hypogonadism.
Here we present a case of Kalmann syndrome in monozygous twins, caused by a previously not described heterozygous mutation c.462C> G: p.I154M in the SOX10 gene in the absence of sensorineural hearing loss. The mutation was inherited from a father who has only isolated anosmia in the phenotype. This mutation was identified during full exome sequencing. This unique observation for Russia shows on the one hand expediency to check SOX10 sequence in addition to the other factors of neuronal migration and differentiation and, on the other hand, the prospect of full exome sequencing in a group of patients with undifferentiated iHH.
Partial androgen resistance syndrome (PAIS) is the most difficult form of disorders/differences of sex development 46,XY (DSD 46,XY) for choosing of patient management. To date, there are no clear biochemical criteria, especially before puberty, that allow differentiating PAIS from other PAIS-like forms of DSD 46, XY, and genetic verification of the partial form of AIS plays an important role. Meanwhile, according to the literature, mutations in the coding region of AR gene have not been identified in more than 50% of patients with suspected AIS. We performed an extensive analysis of the AR gene in a patient with clinical and laboratory signs of AIS and found a deep intron mutation in the AR gene (p. 2450–42G>A). This variant creates an alternative splice acceptor site resulted a disturbance of the AR function. These findings indicate the need for extensive genetic analysis in a cohort of patients with suspected CPA in the absence of mutations in the AR gene using standard methods of genetic diagnosis.
11β-hydroxylase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disorder due to impaired steroidogenesis in the adrenal cortex caused by pathogenic mutations in the CYP11B1 gene. The main clinical manifestations are determined by a deficiency of cortisol, ACTH hyperproduction, excessive androgens secretion and the accumulation of 11-deoxycorticosterone, which leads to the development of arterial hypertension. In the diagnostic search, it is important to take into account the ethnicity of the patient, since the frequency of the disease and the prevalence of mutations differ between ethnic groups. The article presents a clinical case of 11β-hydroxylase deficiency as the result of compound heterozygous mutations in the CYP11B1 gene in a patient of Turkic origin. This case shows the clinical manifestations and the development of complications of 11β-hydroxylase deficiency, the stages of differential diagnosis of patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
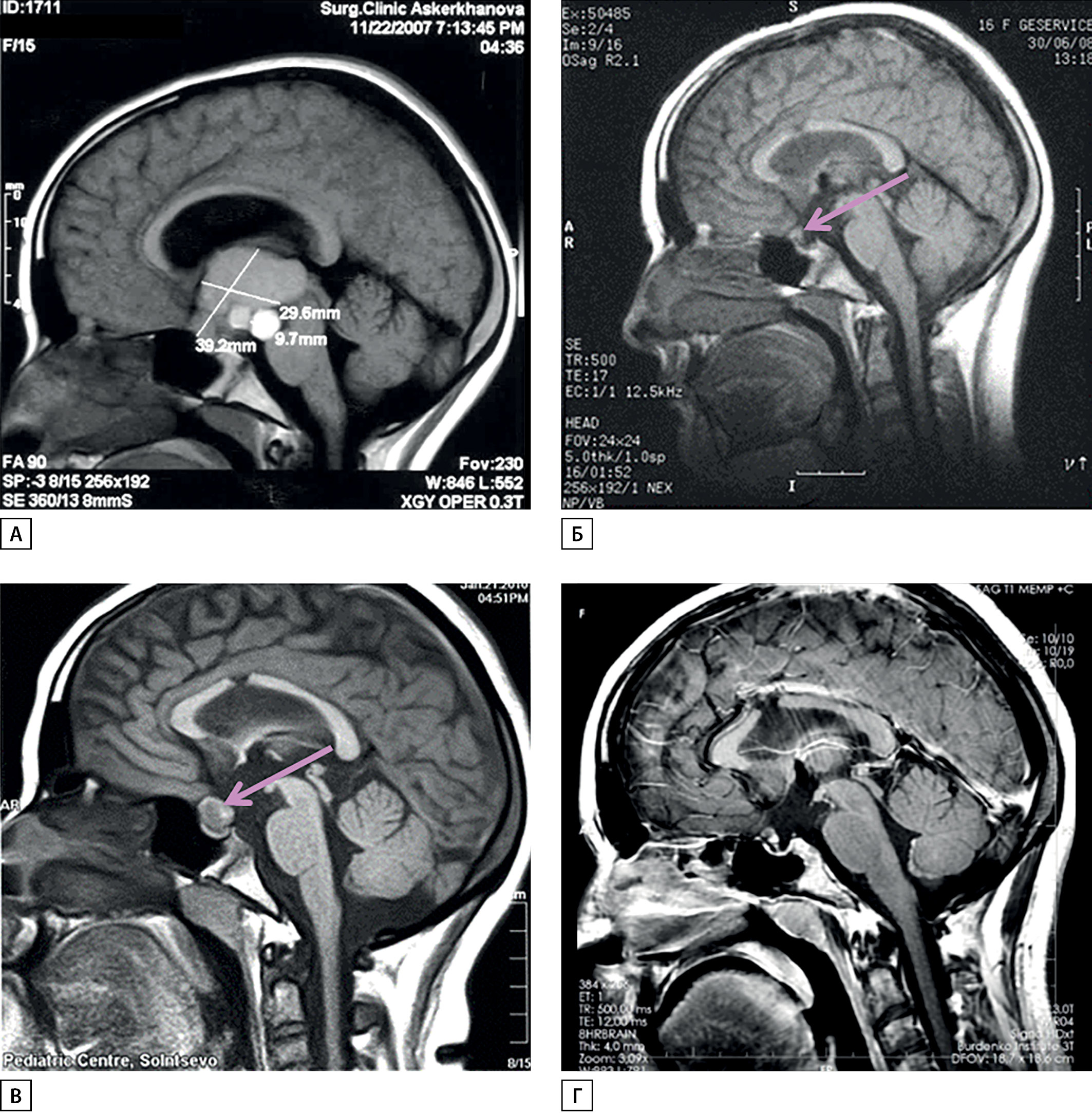
We describe a 15-year girl, who developed panhypopituitarism and diencephalic obesity after surgical excision of craniopharyngioma, followed by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cirrhosis 5 years after surgery. Cirrhosis in this case manifested by hypoxia due to hepatopulmonary syndrome, and despite cure of craniopharyngioma by surgery and radiosurgery treatment and adequate hormonal substitution therapy patient died 9 years after surgery. Growth hormone substitutional therapy in patients with hypopituitarism, and steatohepatitis may decrease liver triglyceride accumulation and prevent end-stage liver disease.
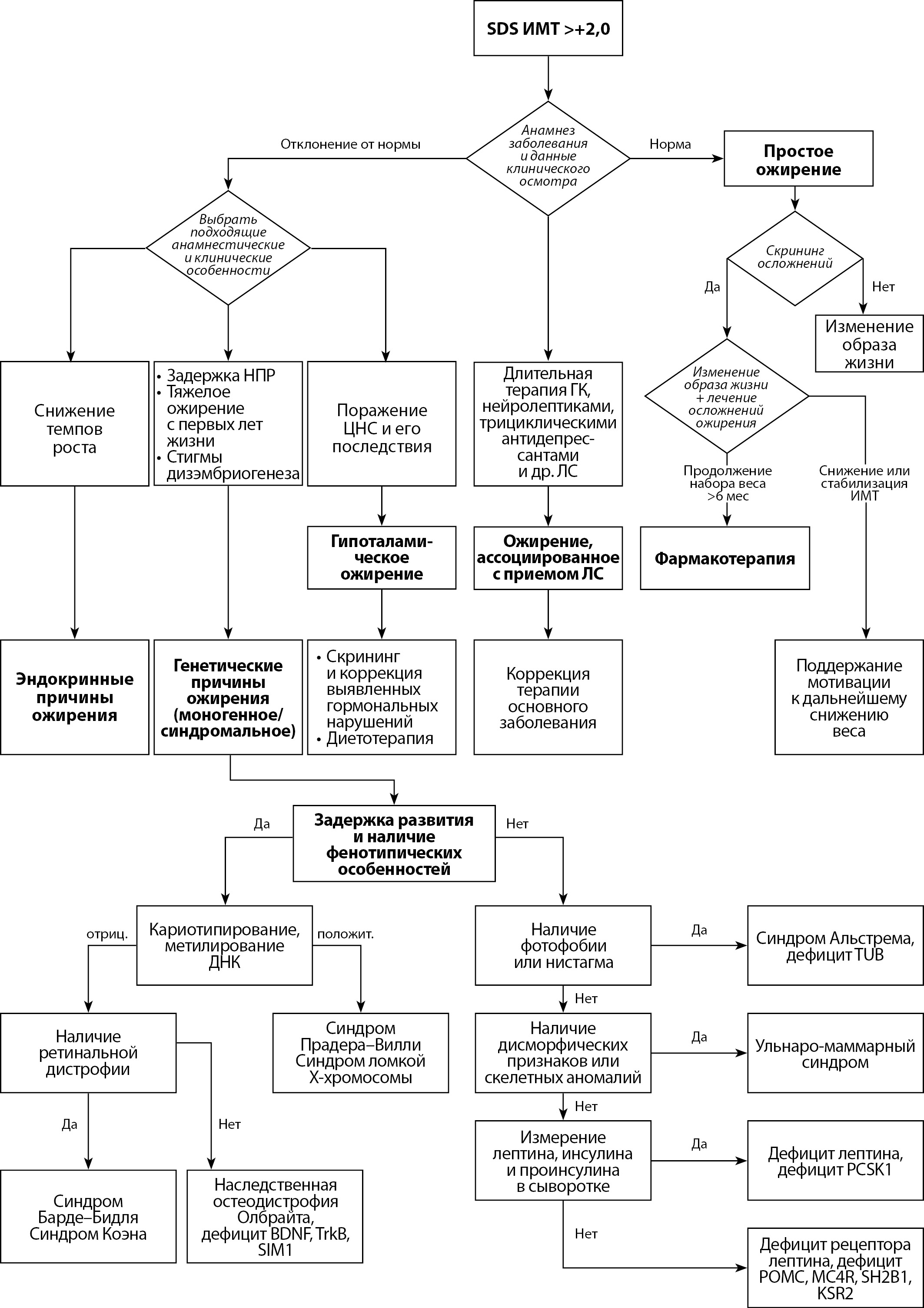
Childhood obesity is an urgent problem of pediatric endocrinology due to the widespread occurrence, the development of metabolic complications and their steady tracking into adulthood. The developed clinical guidelines are the main working tool of the practitioner. They briefly and structurally present the main information about the epidemiology and modern classification of obesity, methods of its diagnosis and treatment based on the principles of evidence-based medicine.
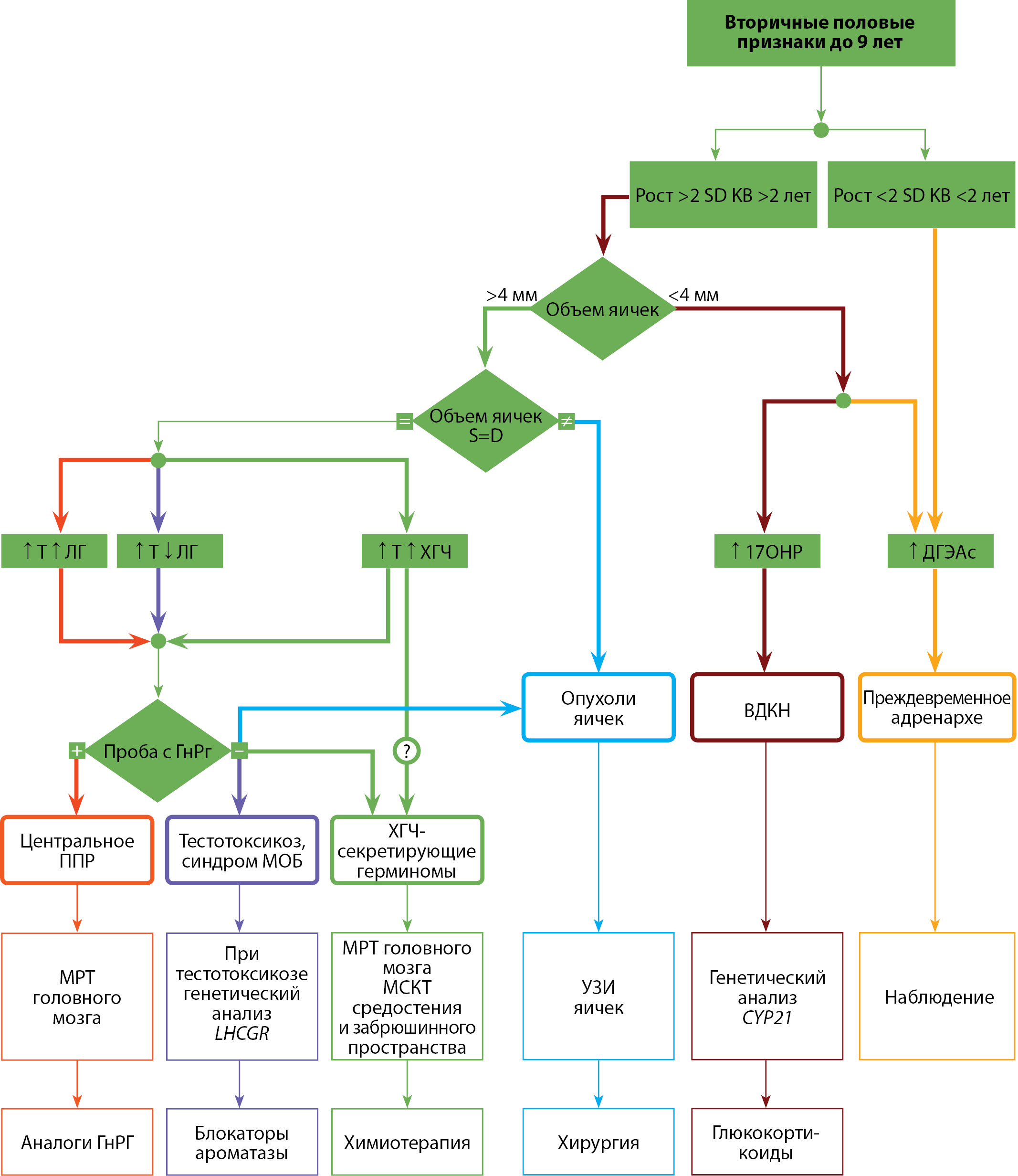
The precocious puberty is an urgent problem of pediatric endocrinology characterized by clinical and pathogenetic heterogeneity. The appearance of secondary sex characteristics before the age of 8 years in girls and 9 years in boys requires timely diagnosis and the appointment of pathogenetically justified treatment in order to achieve the target indicators of final growth and prevent social deprivation. The developed clinical guidelines are the main working tool of the practitioner. They briefly and structurally present the main information about the epidemiology and modern classification of рrecocious puberty, methods of its diagnosis and treatment based on the principles of evidence-based medicine.
Letters from Our Readers
The Letter to Editor presents an analysis of some sections of the clinical guidelines «Diseases and conditions associated with iodine deficiency» published in No. 3 of the journal «Problems of Endocrinology» for 2021. In particular, the discussion deals with the coding of thyroid diseases according to ICD-10, depending on the iodine status of the population of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, as well as issues of diagnosis and treatment, such as «verification» of goiter detected by palpation, or treatment of the vast majority of children, adolescents and adults with potassium iodide. The obstacles to the epidemiological assessment of the iodine status of the population when examining schoolchildren are discussed separately, in connection with the introduction in 2020 of the new regulation, which requires the mandatory use of iodized salt for cooking in school canteens throughout the country.
Obituary
Vladimir Vasilievich Potemkin is one of the leading endocrinologists in our country, the founder and leader of the first course of endocrinology in the USSR (1973–2017), and then the specialized department of the Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov, Honorary Professor of the Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogova, Professor of the Department of Endocrinology of the Medical Faculty, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Worker of the Higher School of the Russian Federation.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2308-1430 (Online)











































.jpg)


