Editorial notice
This article traces the history of the development of radioiodine therapy (RIT) as one of the leading methods for treating thyroid disorders. The relevance of the topic is determined by the high efficacy of RIT in managing thyrotoxicosis and differentiated thyroid cancer, as well as the ongoing efforts to refine dosimetric strategies and molecular imaging techniques. Based on a systematic review of historical publications and monographs from 1923 to 2022, the study analyzes key milestones in the clinical implementation of iodine-131 — from the pioneering experiments of Hertz and Seidlin in the United States in 1937 to the widespread adoption of the method in the USSR beginning in the 1950s and its subsequent advancement at the National Medical Research Center for Endocrinology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. The reviewed literature highlights the significant contributions of Russian researchers to the formation of personalized theranostic approaches and underscores the need for further improvement in planning methods, dynamic treatment monitoring, and the broader expansion of radionuclide therapies for thyroid diseases.
Clinical endocrinology
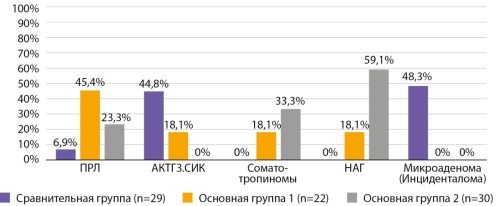
BACKGROUND. Currently, due to the lack of clear criteria for predicting the aggressive course of pituitary adenomas (APA), the search for diagnostic markers is highly relevant. Genetic markers, among others, may serve as such markers since their identification is possible at early stages of the pathological process.
OBJECTIVE. To study the prevalence of genotypic polymorphisms G634C of the VEGFA gene (locus rs2010963), C/T of the TP53_2 gene (locus rs17884159), C/T of the HIF1A gene (locus rs11549465), and G-197A of the IL-17A gene in a sample of patients with APA and their association with the development of various clinical variants of the aggressive course of the disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study included 100 patients with a clinically confirmed diagnosis of pituitary adenoma (main group) and 83 practically healthy individuals (control group). The polymorphism of the studied genes was analyzed using allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with SNP-Express reagent kits in real-time mode ("Sintol", Russia). The interpretation of the results was carried out using the "RotorGene" software of the PCR-RV device. The study also included general clinical, biochemical, and hormonal tests, as well as instrumental and neuroimaging methods, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the chiasmatic-sellar region and statistical analysis.
RESULTS. The study showed that the heterozygous mutation (G/C) of the G634C VEGFA polymorphism was recorded in 21 cases (26%), and the homozygous mutation with a complete replacement of guanine (G) by cysteine (C) at position 634 (C/C) was detected in 4 cases. In patients with invasive pituitary adenomas (PA), the heterozygous variant (G/C) was twice as frequent — 32.7% (n=17) compared to the control group — 15.7% (n=13). The homozygous genotype (C/C) was also more frequently observed in patients with invasive PA growth — 7.7% (n=4) compared to the control group.
The heterozygous variant (C/T) of the HIF1A gene was significantly more common (p=0.02) in patients with invasive adenomas compared to the control group: 25% (n=13) and 9.8% (n=8), respectively. In non-invasive PAs, this genotype was observed three times less frequently. The study of TP53_2 polymorphism (locus rs17884159) showed that in patients with invasive PAs, the frequency of the heterozygous variant (C/T) was significantly higher — 15.4% (n=8) compared to the control group — 4.8% (n=4).
CONCLUSION. The conducted genetic analysis of polymorphisms in the VEGFA, HIF1A, TP53_2, and IL-17A genes revealed significant deviations, confirming their practical significance in the early diagnosis of aggressive pituitary adenomas.
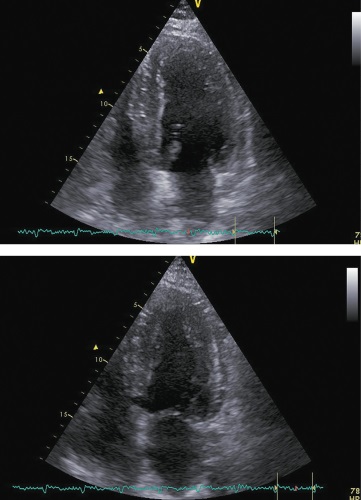
Cortisol-induced dilated cardiomyopathy (CI-DCM) is a rare manifestation of endogenous hypercortisolism (EH). Optimal management of patients with CI-DCM is a major challenge due to the rarity of the pathology and the lack of expert community guidelines. This article describes a case of successful management of a patient with ACTH-secreting pituitary tumor and CI-DCM.
A 44-year-old patient was hospitalized with symptoms of chronic heart failure (CHF) and EH. The diagnosis of non-ischemic myocardial damage with phenotype of DCM was verified by echocardiography and coronary angiography. According to hormonal and imaging tests, and selective blood sampling from the inferior petrosal sinuses, an ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma was diagnosed. A transnasal transsphenoidal adenomectomy was planned. Due to the symptoms of CHF and systolo-diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle (LV), significantly increasing the risk of adverse perioperative cardiac events, the intervention was postponed. Stabilization of the patient’s condition was achieved after 4-month therapy with use of betaAB, ACEI, MRA, diuretics, and steroidogenesis inhibitors. Stabilization of the patient’s condition allowed to perform transnasal transsphenoidal adenomectomy without perioperative complications, with postoperative decrease of ACTH and cortisol levels. Follow-up examinations demonstrated preservation of eucorticism, regression of CHF symptoms. progressive decrease of LV size/volumes with increase of LVEF.
Cortisol hypersecretion can damage myocardium with a phenotype of DCM, with symptoms of CHF being the dominant clinical manifestation of EH. The use of betaAB, ACEI, diuretics, MRA, and steroidogenesis inhibitors is reasonable to control symptoms of CHF and prepare a patient with CI-DCM for surgical intervention. After normalization of cortisol level, regression of CHF symptoms and significant reduction of heart chamber size/volumes with increase of LVEF are noted, which allows to conclude about reversibility of pathologic cardiac remodeling.
This review is an abridged translation of selected chapters of the report “Prevention and control of iodine deficiency in the WHO European Region: adapting to changes in diet and lifestyle”, published by the WHO Regional Office for Europe and the Iodine Global Network (IGN) in 2024. Iodine deficiency, especially mild iodine deficiency, remains a widespread problem in the WHO European Region. Since the last WHO report on iodine deficiency in the Region 15 years ago, much new data on iodine status has become available, especially for vulnerable populations. This review presents data on the iodine status of the population in 53 WHO European Member States (and Kosovo), the adverse effects of mild iodine deficiency and the effectiveness of salt iodization in preventing iodine deficiency. Mainly due to progress in salt iodization, the number of countries with iodine deficiency has decreased from 23 in 2003 to 2 in 2023. Mandatory salt iodization ensures adequate iodine intake in all population groups, with the exception of a few countries where these programs are poorly implemented. The positive cost-benefit ratio for preventing mild iodine deficiency in the European Region is plausible given the high prevalence of thyroid disease and the low cost of salt fortification programs.
This article presents a literature review on the topic of remission of severe neuroendocrine diseases due to adenoma apoplexy. The discussion addresses possible mechanisms underlying apoplexy in pituitary adenomas.
Additionally, two clinical cases of spontaneous remission of acromegaly and Cushing's disease in patients hospitalized at Endocrinology research Centre for neurosurgical treatment are discussed. These cases highlight the need for thorough examination and retesting of patients with hormonally active tumors immediately prior to neurosurgical interventions.
Bones & Adipose tissues diseases
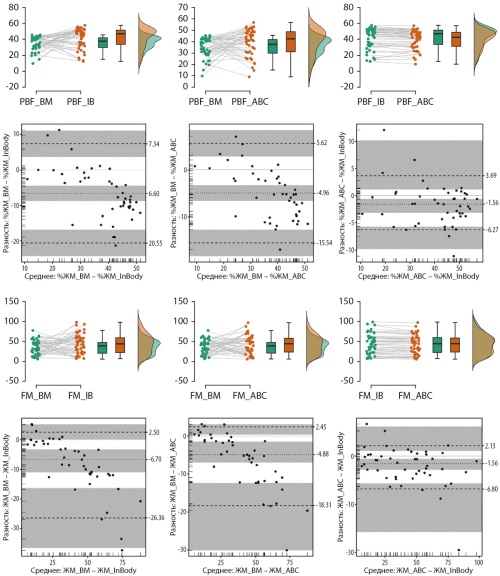
BACKGROUND: Determination of body composition components — muscle and fat mass — is an important step in clinical and epidemiological studies. The most common methods for quantitative determination of body composition are indirect methods. However, the variety of methods and models of devices used makes direct comparison of data at both group and individual levels difficult.
AIM: The aim of the study is to analyze the consistency of estimates of absolute values of fat and lean body mass, as well as the proportion of body fat mass, obtained using bioimpedance analyzers ABC-02 «Medas» (STC Medas, Russia), 770InBody (InBody, Korea) and ultrasound scanner BodyMetrix BX2000 (IntelaMetrix, USA) in a group of men and women.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: An observational, single-center, cross-sectional, uncontrolled study was conducted. The main anthropometric characteristics (height and weight, waist circumference) were measured. Body composition was determined by bioimpedancemetry (BIA) using the octopolar scheme on the 770InBody device and the tetrapolar scheme on the ABC-02 Medass device and ultrasound scanning using the BodyMetrix BX2000 (BM) ultrasound scanner. The absolute (FM) and relative amount of body fat (PBF) and lean body mass were calculated.
RESULTS: A total of 48 people (38 women and 10 men) aged 24 to 74 years were examined. The anthropometric characteristics of the examined subjects were presented in a wide range. A strong correlation was found for all pairs of body composition components: the minimum value for the pair PBF ABC-BM was 0.853 [0.730, 0.913], the maximum was 0.988 [0.977, 0.993] for the pair FM ABC-InBody. Also, significant statistical differences (p<0.001) were found for all pairs of measurements, except for PBF determined by the BIA method. High agreement (CCC>0.95) of BIA estimates of the absolute amount of fat mass was shown, moderate agreement (CCC 0.9–0.95) is characteristic of the PBF determined by different BIA analyzers, and for all other pairs the agreement of measurements can be assessed as weak (CCC<0.90).
CONCLUSION: The best agreement at the group and individual levels was found for FM estimates by two different BIA analyzers (InBody and ABC).
BACKGROUND: The main treatment for primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is parathyroidectomy (PTE), conservative therapy, including bisphosphonates, can be used for preoperative correction of hypercalcemia, as well as to improve bone tissue condition among individuals for whom surgery should be postponed or cannot be performed due to high perioperative risks. The question of the effect of bisphosphonates on bone tissue after surgery remains open.
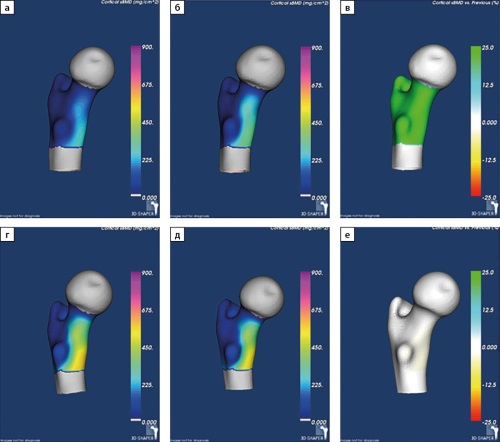
AIM: To study the effect of preoperative bisphosphonate therapy on BMD parameters assessed in DXA and 3D-DXA in patients with PHPT one year after radical PTE.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study was conducted on the basis of the Department of pathology of the parathyroid glands and disorders of mineral metabolism of "Endocrinology Research Center" state-funded research facility of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. The study included 50 patients (2 men, 48 women), divided into two groups depending on the presence or absence of preoperative bisphosphonate (BF) therapy. The methods of DXA and 3D-DXA using 3D-Shaper Medical software were used to evaluate BMD and bone microarchitectonics. The statistical analysis was performed using the R language and the Statistica v.13 package.
RESULTS: At the time of the disease’s manifestation, both groups were comparable in terms of the main indicators of calcium phosphorus metabolism, with the exception of the level of beta-crosslapse, which was higher in the group without preoperative BPh therapy (p<0,001). There were also no differences in the parameters of DXA and 3D-DXA. After surgery, both groups showed a comparable increase in BMD based on the results of DXA in the main parts of the skeleton and 3D-DXA in the femur. Changes at the level of the statistical trend were obtained for the 3D-DXA parameters, the final absolute values of which were slightly higher in the second group, including the thickness of the cortical layer in the femur as a whole and in the neck. When comparing the results of DXA before and after PTE in patients receiving BPh, statistically significant differences in absolute BMD values were obtained only in the lumbar spine (p<0,001).According to 3D-DXA data, statistically significant differences were found only in the volume of mineral density of the trabecular bone of the femur as a whole (p=0,001).
When analyzing up to — in the second group, statistically significant differences in absolute BMD values were observed in the lumbar region (p<0,001), in the hip as a whole (p<0,001) and in its neck (p=0,001).According to 3D-DXA data, statistically significant differences were found in three of the eight analyzed indicators, the volume of mineral density of the trabecular bone of the femur as a whole and in the neck (p<0,001 for both), as well as the volume of mineral density of the cortical bone in the neck, (p=0,001).
CONCLUSION: The 3D-DXA method allows us to evaluate not only BMD, but also its microarchitectonics, which is important for predicting the risk of fractures in patients with PHPT. Studies have shown that preoperative BPh therapy can negatively affect the recovery of BMD after PTE, especially in cortical bone tissue. Further studies are needed to confirm these data and clarify the effect of CF on the postoperative course of PHPT.
Pediatric Endocrinology
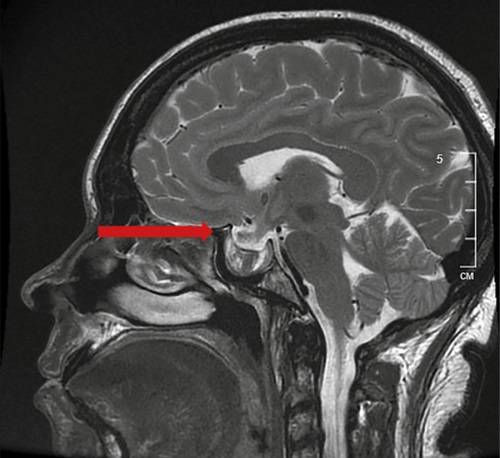
Cushing’s disease (CD) is the leading form (75–80%) of the endogenous hypercortisolism (EH) in adolescents. Despite the obvious clinical manifestations, the diagnosis of CD is complicated because of the need of several research methods, the risk of false-positive and false-negative results, difficulties in interpretation and the low percentage of MR-imaging in children. The present patient had noted excessive weight gain since the age of 10 years, a decrease in growth rate was detected retrospectively, absolute short stature developed by the age of 14.5 years. An examination at the age of 15 revealed an inversion of the circadian cortisol rhythm (9:00 378.4 nmol/l, 23:00 598.9 nmol/l), an increase in the cortisol level in saliva at 23:00 (20.32 nmol/l) and excretion in urine (981.5 mcg/day). The overnight dexamethasone test (ODT) was positive (cortisol 44.26 nmol/l), ACTH was in the “gray zone” (22.19 pg/ml). MRI with contrast showed signs of a heterogeneous pituitary gland structure. When patient was re-examined at 15.5 years the inversion of the circadian rhythm of cortisol was accompanied by absolute hypercortisolemia (9:00 843.4 nmol/l, 23:00 929.4 nmol/l), ODT became negative (cortisol 235 nmol/l), ACTH level remained in the “gray zone” (25.1 pg/ml). MRI with contrast showed pituitary adenoma 6×4 mm. An ACTH level gradient between the left inferior petrosal sinus and peripheral blood of 13.3 confirmed CD. After transsphenoidal adenomectomy, a cortisol level of 39.4 nmol/l indicated remission with a low risk of relapse; subsequently a reverse development of EH symptoms were noted. Postoperative diabetes insipidus and primary hypothyroidism required replacement therapy.
Reproductive Endocrinology
BACKGROUND: To optimize androgen replacement therapy for male hypogonadism to improve reproductive prospects.
AIM: To compare the effectiveness of restoring the quality of ejaculate in men receiving androgen replacement therapy (AZT) and patients receiving course combination therapy with testosterone and chorionic gonadotropin (AZT/HG).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In observational prospective study was included 53 men observed at The National Medical Research Center for Endocrinology and AZT (n=19) or AZT/HG (n=34) more than 5 years, followed by stimulating gonadotropin therapy. The qualitative parameters of ejaculate were evaluated in all patients. The basic level of statistical significance was p<0,05.
RESULTS: The patient groups were comparable in age, BMI, duration of therapy used, type of testosterone preparation, as well as the etiology of hypogonadism. Sperm concentration in the AZT group there was a statistically significant negative dynamics, while in the ART/HG group, there were no statistically significant differences in the dynamics of sperm concentration. Statistically significant differences in the value of sperm concentration change were revealed. In both groups was observed statistically significant negative dynamics for sperm motility and morphology. There were no statistically significant differences in the value of changes motility and sperm morphology in both studied groups.
CONCLUSION: Course combination therapy with testosterone and chorionic gonadotropin is characterized by better results for sperm concentration restoration compared with androgenic replacement therapy. For the restoration of sperm motility and morphology both methods do not show satisfactory results.
BACKGROUND: Combined treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) may have an impact on the reproductive health of patients, in particular on the ovarian reserve (OR) of childbearing-age women. However, knowledge in this area is still insufficient to create general recommendations and an algorithm for managing this cohort of patients based on their current reproductive status and desire to realize their reproductive potential.
AIM: To assess ovarian function and OR using anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol (E2) in dynamics in the early follicular phase in women of reproductive age receiving combined treatment for DTC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: In a single-center prospective non-comparative study, the clinical and morphological, anamnestic and laboratory parameters of patients receiving combined treatment for DTC were analyzed. The levels of AMH, FSH, LH and E2 were determined in dynamics – after surgical treatment but no later than one month before radioiodine therapy (RAIT), as well as 3 and 6 months after RAIT on the background of suppressive therapy.
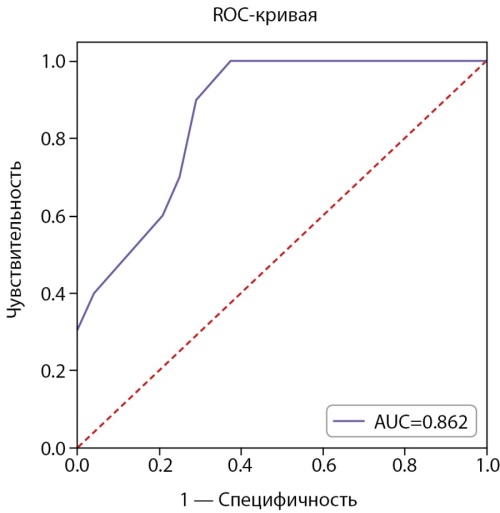
RESULTS: A total of 39 women aged 18 to 40 years with a median age of 32 years [27; 37] undergoing combined treatment for DTC were enrolled in the study. The frequency of transient menstrual cycle disturbances after surgery was 18%, and after RAIT — 38%. According to the post-operative DTC status the majority of patients belonged to ATA intermediate-risk group (69%). In addition, 72% of patients received thyroid hormone withdrawal for a period of 4 weeks as a preparation for RAIT. The average activity of 131I was 3720 MBq [3050; 3838]. The levels of FSH and LH did not differ significantly before and after RAIT (R=NS). The level of E2 decreased significantly 3 months after RAIT (P<0.010), further increasing in 6 months to almost the initial values (P=NS). The level of AMH decreased significantly 3 and 6 months after RAIT compared with baseline values (P<0.001). The median AMH before the treatment was 4.10 ng/ml [2.34; 5.82], the nadir of AMH was observed after 3 months — 2.09 ng/ml [1.05; 3.05], and after 6 months AMH increased to 2.31 ng/ml [1.42; 3.37]. In 29% of patients, the AMH level decreased below the reference after 3 months. The predictor of AMH level below 1.2 ng/ml (reflecting reduced OR) 3 months after RAIT was the patient’s age before RAIT. Using the Juden index, a cut-off point of 31 years was determined.
CONCLUSION: The level of AMH decreases significantly after RAIT for DTC, which indicates the effect of the therapy on OR, while age at the time of RAIT is the main predictor of AMH level below 1.2 ng/ml after 3 months.
A woman spends more than a third of her life in a state of deficiency of female sex hormones. According to WHO, in most countries of the world the life expectancy of women after 50 years fluctuates between 27 and 32 years. Every year the number of women entering the menopause period increases. In 1990, 467 million were in the postmenopause period, by 2030 the number will reach 1.2 billion. Menopause, not being a disease itself, leads to a violation of the endocrine balance in the body, causing not only «classic» problems in life (vasomotor symptoms, psychological health disorders, urogenital disorders, osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases), but also changes the appearance of women — the dermatological status of the patient is worse than the age group. The article presents modern data on rational MHT. Particular attention is paid to the issues of efficacy, tolerability and safety of combined MHT containing estrogen and gestagen, based on the results of current studies and in accordance with the position of national and international clinical guidelines. A clinical case is used to demonstrate the tactics of managing a woman in menopause.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2308-1430 (Online)








































.jpg)


