Editorial notice
Diabetic neuroarthropathy (DNOAP, Charcot’s foot) is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus, the genesis of which is not fully understood. In most cases, this pathology is diagnosed late, which leads to the development of severe deformities of the foot, up to the loss of support ability of the limb. There is no single hypothesis for the formation of Charcot’s foot, but there are factors predisposing to its development, as well as a few likely provoking events. Excessive formation and accumulation of end products of glycation may play an important role in the pathogenesis of this complication of diabetes. End products of glycation (AGE) are a variety of compounds formed as a result of a non-enzymatic reaction between carbohydrates and free amino groups of proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. There are various factors that lead to the accumulation of AGE in the human body. Allocate endogenous and exogenous factors. The former include certain diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, renal failure, which accelerate glycation processes. Exogenous factors leading to the formation of lipo-oxidation and glyco-oxidation products include tobacco smoke and prolonged heat treatment of food.
This review provides information on the role of glycation end products in the development and progression of complications in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Clinical endocrinology
Iodine deficiency disorders is a sweeping term that includes structural and functional impairment of the thyroid gland.
These clinical guidelines include algorithms for the diagnosis and treatment of euthyroid goiter and nodular/ multinodular goiter in adults and children. In addition, these clinical guidelines contain information on methods for an adequate epidemiological assessment of iodine deficiency disorders using such markers as the percentage of goiter in schoolchildren, the median urinary iodine concentration, the level of neonatal TSH, the median thyroglobulin in children and adults. As well from these clinical guidelines, you can get to know the main methods and groups of epidemiological studies of iodine deficiency disorders.
This literature review focuses on the normal adrenal gland anatomy and typical imaging features necessary to evaluate benign and malignant lesions. In particular, adenoma, pheochromocytoma, metastases and adrenocortical carcinoma were discussed as some of the most common lesions. For this purpose, a review of relevant local and international literature sources up to January 2021 was conducted.
In many cases, adrenal incidentalomas have distinctive features allowing characterization using noninvasive methods. It is possible to suspect a malignant nature and promptly refer the patient for the necessary invasive examinations in some cases. Computed tomography, especially with intravenous contrast enhancement, is the primary imaging modality because it enables differential diagnosis. Magnetic resonance tomography remains a sensitive method in lesion detection and follow-up but is not very specific for determining the malignant potential. Positron emission computed tomography also remains an additional method and is used mainly for differential diagnosis of malignant tumors, detecting metastases and recurrences after surgical treatment. Ultrasound has a limited role but is nevertheless of great importance in the pediatric population, especially newborns. Promising techniques such as radiomics and dual-energy CT can expand imaging capabilities and improve diagnostic accuracy.
Because adrenal lesions are often incidentally detected by imaging performed for other reasons, it is vital to interpret such findings correctly. This review should give the reader a broad overview of how different imaging modalities can evaluate adrenal pathology and guide radiologists and clinicians.
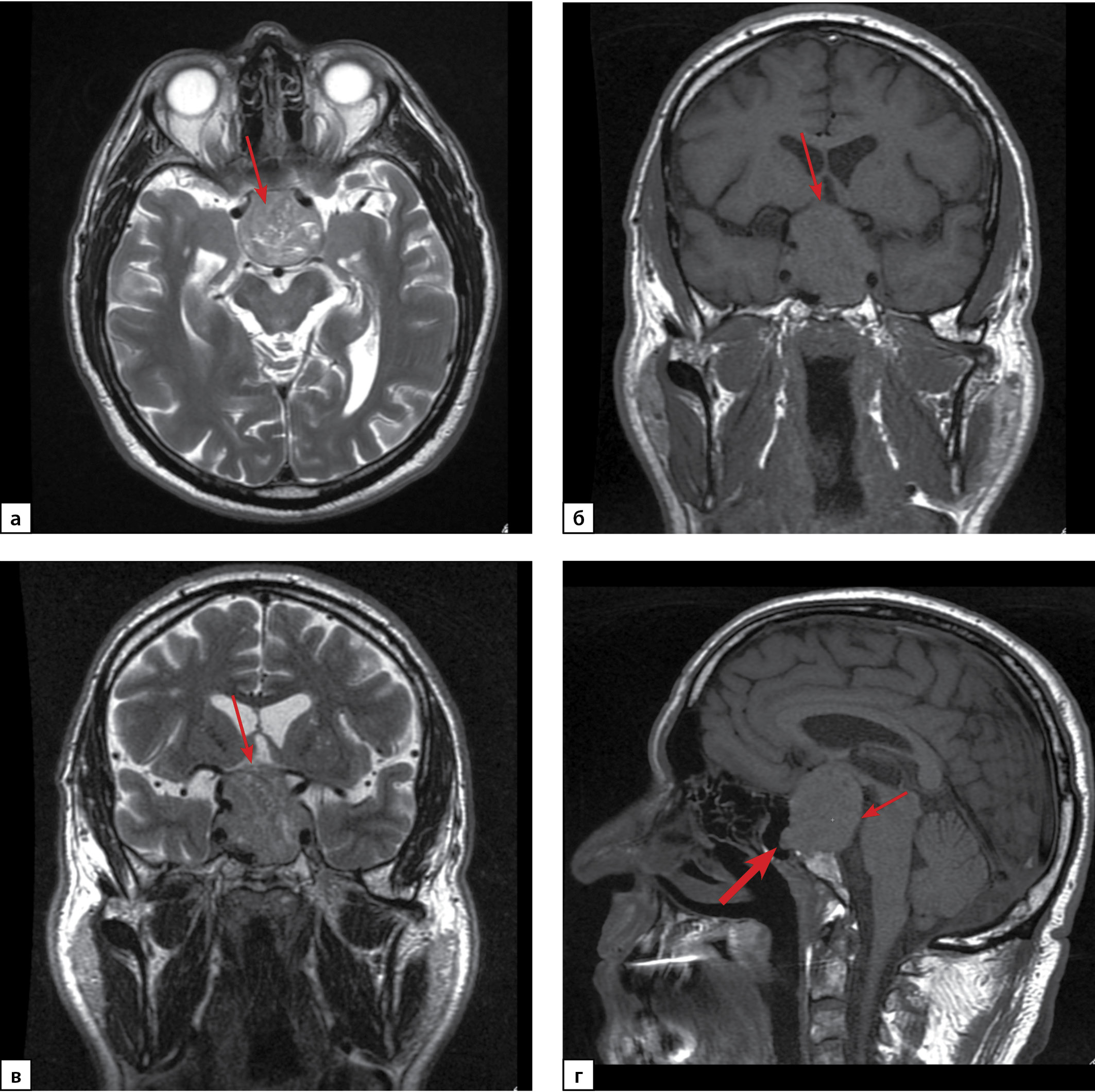
Functioning gonadotroph adenomas are rare pituitary tumors secreting one or two gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and/or luteinizing hormone (LH)), which are hormonally active. In the majority of cases, gonadotroph tumors are endocrinologically “silent” and make up more than a half of non-functioning pituitary adenomas. In this article we describe a rare clinical case of LH/FSH-secreting pituitary macroadenoma with bitemporal hemianopsia in a 62-year-old man. The patient underwent transnasal transsphenoidal adenomectomy, leading to remission. The distinctive feature of this case is the presence of secondary erythrocytosis due to endogenous hyperandrogenism, which required several blood exfusions to normaliza the level of hematocrit before surgery. It is noteworthy that clinical signs of erythrocytosis were present long before visual impairment. This clinical case demonstrates difficulties in the early diagnosis of functioning gonadotroph adenomas.
Bones & Adipose tissues diseases
BACKGROUND: Older adults with osteoporosis (OP) and high risk of falls are the most vulnerable group of patients with respect to the development of fractures. Falls and fractures in elderly patients with OP are associated with geriatric syndromes and worse functional status.
AIM: To аssess comorbidity and geriatric status in elderly and senile patients with and without OP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study included 607 patients over 60 years of age hospitalized in the geriatric department. According to the presence of OP, the patients were divided into 2 groups: group 1 — patients with OP (n=178, 29.3%), group 2 — patients without OP (n=429, 70.7%). All patients underwent a general clinical study, an assessment of comorbidity according to the Charlson index, and a comprehensive geriatric score.
RESULTS: OPs had 178 (29.3%) patients, more often these were women. 55.6% of patients with OP were disabled. Age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, osteoarthritis, anemia, thyroid disease, varicose veins were significantly more common in patients with OP. With almost all of these diseases, a univariate analysis revealed an association with OP. Geriatric syndromes such as frailty, hypodynamia, malnutrition, polypharmacy, urinary incontinence were significantly more common in group 1 patients. Patients with OP were more likely to live alone and use mobility aids compared to patients without OP.
The univariate analysis demonstrated that OP is associated (OR 1.54 to 2.00) with frailty, hypodynamia, the use of aids in movement, sleep disorders, sensory vision deficiency, urinary incontinence. The Functional status of patients with OP was worse compared to patients without OP. Patients with OP suffered more fractures, and vertebral fractures were significantly more frequent.
CONCLUSION: Patients with OP have a high comorbidity, a burdened geriatric status. In elderly patients, it is necessary not only to screen and diagnose OP, to assess the risk of 10-years probability of major pathological fractures using the FRAX algorithm, but also to conduct a comprehensive geriatric assessment to diagnose geriatric syndromes that weaken the course of OP and lead to more serious consequences.
Pediatric Endocrinology
Gonadotropin-dependent precocious puberty (central) is a condition resulting from the early (up to 8 years in girls and 9 years in boys) reactivation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. An increase in the secretion of sex steroids by the gonads in this form is a consequence of the stimulation of the sex glands by gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland. In the absence of central nervous system abnormalities, CPP is classified as idiopathic and as familial in some cases, emphasizing the genetic origin of this disorder. Loss-of-function mutations in Makorin Ring Finger Protein 3 (MKRN3) are the most common identified genetic cause of central precocious puberty compared to sporadic cases. In the present study we performed the first descrition of 3 family cases of central precocious puberty duo to novel MKRN3 gene mutation detected by NGS in the Russian Federation.
Congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH) is a rare disorder characterised by lack of pubertal development and infertility, due to deficient production, secretion or action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Clinically, there are variants of CHH with hypo-/anosmia (Kalman syndrome) and normosmic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Given a growing list of gene mutations accounting for CHH, the application of next generation sequencing (NGS) comprises an excellent molecular diagnostic approach because it enables the simultaneous evaluation of many genes. Biallelic mutations in GNRHR gene lead to the development of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with normosmia. In this paper, we describe 16 patients with proven GnRH resistance and estimate the frequency of pathogenic variants in the GNRHR gene in the Russian population.
CHARGE syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disease caused by CHD7 gene mutations. Individuals with CHARGE display a wide spectrum of clinical features. It might be presented only as a delay puberty, which does not require any hormone replacement therapy to severe CHARGE phenotype, requiring a multidisciplinary therapeutic approach. Wild spectrum of clinical presentation can be seen even among the patients with identical mutation. Diagnosis might be suspected by a combination of major and minor clinical criteria of this disorder, but molecular genetic analysis is mandatory for final verification. Accurate diagnosis is essential to informing patients about all possible clinical features, reproductive status and choosing the correct treatment approach. The most common endocrine abnormality in patients with CHARGE syndrome is the disturbance in gonadotropins function ranged from delay puberty to persistent hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with different olfactory phenotypes, resulted by specific role of CHD7 in GnRH neuronal embryogenesis.
We describe a familial case of CHARGE syndrome with significant intrafamilial clinical heterogeneity due to CHD7 gene mutation.
Mutations in the gene DHH are an extremely rare cause of disorders of sex development 46,XY (DSD,46XY). The article describes the clinical cases of two unrelated patients with gonadal dysgenesis 46,XY with female phenotype. By using a next generation sequencing method, in both cases the same biallelic variant substitution c. 419T>G in the DHH gene was revealed. Taking into account the data on the role of DHH in the formation of the nervous system, the diagnosis of minifascicular polyneuropathy at the preclinical stage was confirmed in both cases. These cases demonstrate the value of using NGS, which allows simultaneous analysis of a wide range of candidate genes in DSD and the diagnosis of comorbidities before the development of the clinical picture. These are the first descriptions of patients with mutations in the DHH gene in the Russian population.
Reproductive Endocrinology
BACKGROUND: The increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), the high probability of unfavorable pregnancy outcomes for the mother and the fetus, as well as a number of long-term consequences in GDM are a serious medical and social problem and require the need for its prevention by correcting risk factors, timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
AIM: Analysis of risk factors for the development of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), the relationship between GDM, the course and outcomes of pregnancy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Retrospective analysis of 79 case histories of patients with confirmed GDM in the period from 2015 to 2017.
RESULTS: In the structure of risk factors for mother and fetus, age over 30 years (73.1%), burdened heredity for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (30.8%), mother’s pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI) (overweight / obesity (26.9%)) had the greatest impact. Among the complications of pregnancy, the most common was the caesarean section (47.4%). The incidence of other complications (macrosomia (9%), premature birth (7.7%), congenital malformations of the fetus (5.1%), preeclampsia (5.1%) was lower than the average frequency of these complications in GDM, described in the literature. Nevertheless, it is 1.5–2 times higher than the average population indicators. In the course of statistical analysis of the data it was revealed, that the higher the mother’s pre-pregnancy BMI, the lower the Apgar score for the first minute in the newborn.
CONCLUSION: Women with GDM require intensive monitoring of the course of pregnancy and timely hospitalization for planned delivery, and the provision of competent obstetric benefits.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2308-1430 (Online)














































.jpg)


